With a surge in Ethereum staking, how will EIP-7514 address staking-related issues?
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

With a surge in Ethereum staking, how will EIP-7514 address staking-related issues?
EIP-7514 proposes mitigating the rapid surge in ETH staking by adjusting the validator growth rate.
By Ebunker
Rapid Growth in Ethereum Staking
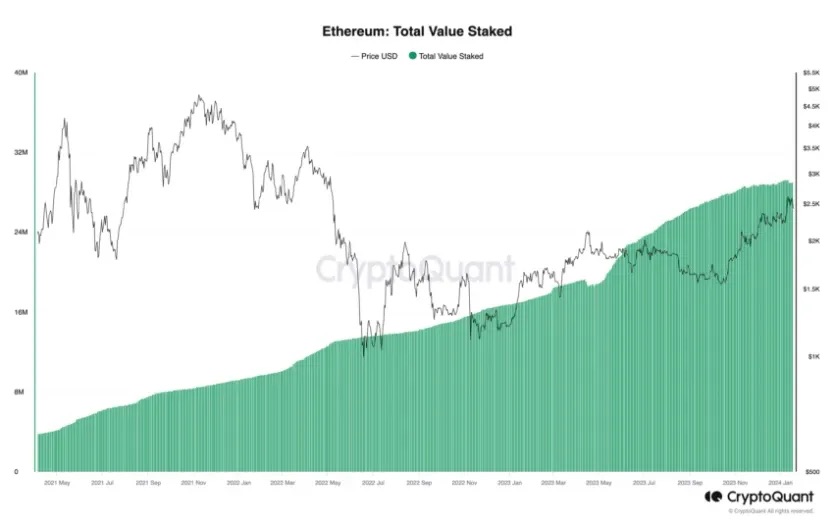
Despite the activation of staking withdrawals following Ethereum's Shapella upgrade, the total staked amount has not declined. Currently, the Ethereum network hosts 898,110 active validators, with a staggering 28.8 million ETH staked—accounting for 24% of the total Ethereum supply—reflecting widespread adoption and trust in the PoS validation mechanism.
According to Ebunker, Ethereum’s annual inflation rate stands at -0.03%, while the recent 7-day staking yield is approximately 5.04%. This deflationary trend combined with attractive staking rewards has bolstered long-term confidence among ETH holders, encouraging them to earn passive income through staking. This trend also aligns with the growing stability and maturity of the Ethereum ecosystem.
Ethereum staking aims to enhance network security and stability while reducing environmental impact, positioning Ethereum blockchain development at the forefront of decentralized applications and enabling secure, transparent digital transactions. However, the surge in staking volume was previously unforeseen and now poses potential risks to the Ethereum network. As a result, Ethereum developers are considering EIP-7514, a proposal that could reshape the future of Ethereum staking.
Risks of Over-Staking on Ethereum
The major concern with over-staking stems from the pressure caused by a sharp increase in validators on the Ethereum network. As more participants join staking, both the number of validators and their associated responsibilities grow continuously. This leads to increased communication overhead, expansion of stakeholders’ ledger (the Beacon Chain), traffic spikes, network congestion, and longer transaction processing times.
As staking levels rise, the strain on the consensus layer responsible for transaction validation grows exponentially. While high staking ratios can theoretically enhance network security, these benefits diminish when staking surges rapidly within a short timeframe.
As more ETH gets staked, staking rewards are distributed across an increasing number of validators, leading to declining individual returns. However, the high profitability of Miner Extractable Value (MEV) and the appeal of liquid staking tokens continue to drive additional staking growth. If this trend continues unchecked, an ever-higher proportion of ETH will be locked up. Therefore, Ethereum must carefully assess this situation to ensure the durability and stability of its network.
How Will EIP-7514 Address Ethereum’s Staking Issue?
EIP-7514 proposes mitigating the rapid spike in ETH staking by adjusting the validator growth rate. It suggests modifying the epoch churn limit—switching from the current exponential growth model to a controlled linear growth model.
The epoch churn limit is a parameter that caps the number of validators joining or exiting the Ethereum network during each epoch. Currently, the number of nodes entering or leaving per epoch is set at 12 and increases slowly as the total validator count grows.
With the proposed change, Ethereum would reduce the rate at which new validators can join—from a variable value (currently around 12) down to a fixed cap of 8 per epoch—slowing the surge in ETH staking. However, the number of validators exiting the network per epoch remains unaffected by this EIP and stays tied to the overall validator count (currently capped at 12 per epoch).
The reasoning is straightforward. According to Ethereum core developer Dankrad Feist, ETH staking could reach 50% of the total supply by May 2024 and potentially approach 100% by December 2024. While high staking levels may theoretically improve security, reaching such levels too quickly risks destabilizing network balance, overburdening the consensus layer, and depleting the available on-chain ETH supply. Implementing EIP-7514 would effectively curb excessively fast growth in staking volume.
EIP-7514 aims to slow the expansion of the active validator set. By capping the size of the validator set, it gives the Ethereum team breathing room to develop long-term solutions. Controlling validator set size is critical for future developments such as Single Slot Finality (SSF) and P2P network traffic management. This ensures the Ethereum network remains healthy and operates as planned, without impacting those already running validators.
Impact of EIP-7514 on Ethereum
EIP-7514 cannot immediately resolve the technical and financial challenges brought by the surge in staking. By fixing the maximum churn limit, it restricts the number of validators entering or leaving the network per epoch, temporarily slowing staking growth and buying time to research long-term fixes. Since the churn limit for validators exiting the network remains dynamic, it is unaffected by this proposal—ensuring effective reward distribution and preventing excessively long withdrawal queues.
Because the implications of staking growth were not fully anticipated when staking was first introduced to the Ethereum network, EIP-7514 serves only as a temporary measure. Setting a hard cap on validator churn makes it harder for new validators to join each epoch, meaning it would take longer for staking levels to climb to higher proportions. If the validator activation queue remains saturated and demand for staking remains unchanged, staking levels will still eventually rise significantly over time.
However, EIP-7514 provides the Ethereum development team sufficient time to explore long-term solutions to the staking issue. Potential long-term approaches currently under consideration include moderately reducing staking yields, implementing MEV burning, promoting greater participation from liquid staking providers to reduce Lido’s dominance, and increasing the required ETH amount per validator. However, since these solutions remain untested and blockchain technology continually evolves with new challenges, deploying them without a thorough understanding of their implications could lead to unpredictable second-order effects.
Community Reaction and Discussion
EIP-7514 has been one of the key topics discussed within the Ethereum community during the 2024 Dencun upgrade period. Currently, community sentiment toward EIP-7514 is mixed.
On one hand, supporters view EIP-7514 as a practical step to control rapid staking growth and alleviate network load. Implementing it before long-term solutions are ready could ease immediate pressures and make subsequent technical upgrades smoother. On the other hand, critics argue that EIP-7514 was hastily proposed without adequate consideration. They point out that the urgency to limit validator growth does not align with the steadily shrinking activation queue and question whether the proposal might compromise Ethereum’s commitment to network neutrality.
Nonetheless, the convergence of diverse viewpoints within the community reflects a collective commitment to addressing challenges and ensuring Ethereum remains resilient and adaptable within its evolving ecosystem. Ongoing discussions will help guide the Ethereum development team in conducting more detailed research and development to solve staking issues without harming other network components.
Summary
The debate surrounding EIP-7514 highlights Ethereum’s dynamic governance and how the community proactively addresses emerging issues. EIP-7514 seeks a delicate balance between fostering staking growth, maintaining network efficiency, and ensuring Ethereum’s long-term sustainability. It sets a precedent for handling unforeseen challenges, playing a crucial role in curbing excessive ETH staking growth and providing the community with valuable time to develop viable alternatives. Ultimately, EIP-7514 represents an important step toward securing Ethereum’s long-term stability and prosperity.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News












