With the rising momentum in the Bitcoin ecosystem, which Layer2 projects are worth watching?
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

With the rising momentum in the Bitcoin ecosystem, which Layer2 projects are worth watching?
What are the current development trends in the Bitcoin L2 sector, and what early signals are worth paying attention to?
Author: Web3CN
Over the past three months, early inscription projects such as Ordinals have driven a surge across the entire sector, with star tokens linked to inscriptions continuously setting new price records. This has also fueled strong interest in inscription concepts on SATS, RATS, and various other public blockchains.
At the same time, sharp criticisms from Bitcoin Core developer Luke Dashjr toward inscriptions like ORDI have poured cold water over the inscription market, prompting renewed reflection and exploration into how inscriptions can coexist healthily and sustainably with Bitcoin.
Against this backdrop, the trend of "L2-ification" within the Bitcoin ecosystem appears unstoppable. Layer 2 solutions not only resolve long-standing complaints about Bitcoin's so-called "junk transactions," but also enable programmability that powers DeFi applications such as swaps, lending, and liquidity mining—offering vast potential. So what trends are currently shaping the Bitcoin L2 landscape, and what early opportunities are worth watching?
The Trend Toward Bitcoin “L2-ification”
As the Bitcoin inscription sector continues to heat up, manually participating in new on-chain inscription projects has quickly become an overcrowded red ocean. From a narrative perspective, however, inscriptions differ from previous large-funded or VC-dominated projects by offering broader access beyond just OGs and whales, allowing more everyday users to participate.
Yet the Bitcoin network at the heart of this inscription frenzy faces significant challenges. The most visible issue is network congestion and soaring transaction fees. Since inscriptions resemble NFTs—allowing users to record arbitrary data onto the blockchain—and Bitcoin transaction fees are based on data size, inscription users often opt for lower fees.
This means they’re willing to wait longer for confirmation, making their transactions easily displaced by higher-priority Bitcoin transfers.
Consequently, these massive volumes of low-fee inscription transactions flood Bitcoin’s mempool—the area storing all valid transactions awaiting inclusion on-chain.
According to crypto KOL bitrabbit.btc, Bitcoin accumulated 87 million UTXOs over its first 14 years, but after BRC20 trading began on April 24, that number surged to 140 million within roughly seven months. Of the over 50 million newly added UTXOs, 40 million were tiny transactions ranging from 100 to 1,000 satoshis.
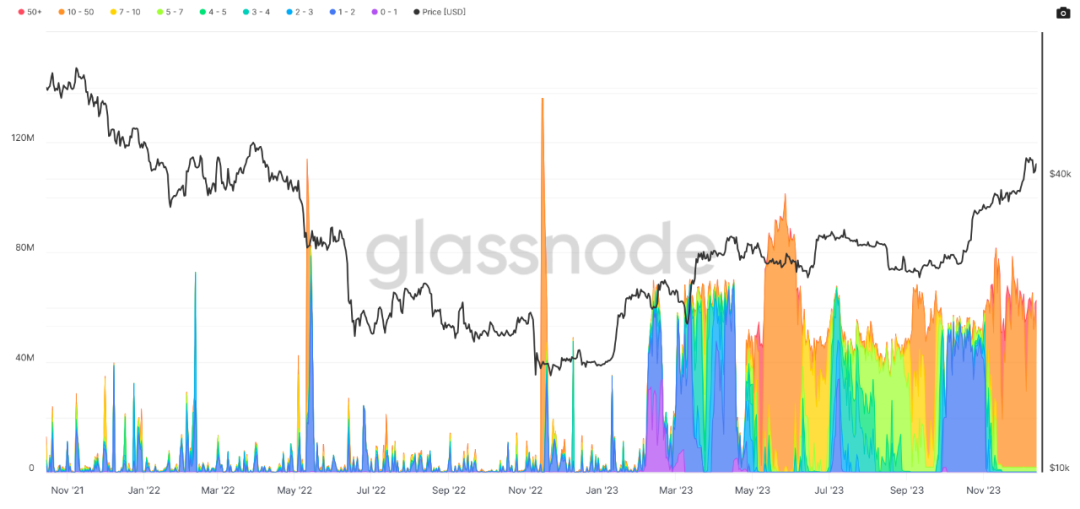
As shown in the chart above, since their launch in February 2023, inscriptions have consistently been the primary consumer of Bitcoin block space. The mempool has remained full since February and remains at historically high levels to date.
This persistent congestion prevents Bitcoin from clearing its mempool effectively, which remains near all-time highs in terms of stored data.
Given current Bitcoin network rules—particularly the anti-dust attack measure requiring each UTXO to contain at least 546 satoshis—most of these pending small-value inscription transactions are effectively equivalent to DDoS-style spam. Many may never be confirmed or broadcasted on-chain.
“These small UTXOs will mostly never be spent, instead sitting forever inside Bitcoin nodes, wasting tens or even hundreds of billions of dollars in hardware and electricity resources over the coming decades.”

This is precisely why Bitcoin Core developer Luke Dashjr has publicly criticized ORDI, inscriptions, and BRC20 so sharply—calling them out for exploiting vulnerabilities in Bitcoin Core to flood the blockchain with junk data.
Thus, despite the inscription market surpassing tens of billions in value with no signs of slowing, traditional inscription projects issued directly on the Bitcoin mainnet face growing constraints due to network congestion and accusations of generating “junk transactions.” These issues pose critical barriers to further scaling.
In contrast, Bitcoin L2 solutions stand out—they alleviate network congestion and eliminate spam transaction concerns by batching transactions off the main chain, while also enabling a range of DeFi use cases such as swaps, lending, liquidity mining, and staking through enhanced programmability.
Overview of Bitcoin L2 Projects
Overall, as building a thriving DeFi application layer on Bitcoin gains traction as a compelling new narrative, Bitcoin L2 projects have emerged as key vessels carrying the hopes of Bitcoin supporters. Beyond well-known older projects like Stacks, RSK, and Liquid, newer approaches such as BitVM and BEVM offer fresh perspectives.
Stacks: The Smart Contract Layer for Bitcoin
As a second layer for Bitcoin, Stacks operates both anchored to the Bitcoin blockchain and as an independent protocol that introduces Ethereum-like smart contract functionality. Transactions are permanently settled on the BTC blockchain, unlocking programmability for Bitcoin and enabling new possibilities for DeFi and NFT applications.
From a system architecture standpoint, Stacks has its own chain, compiler, and programming language, running in sync with Bitcoin to ensure transaction validity and integrity.
However, it uses a “pegging” mechanism for cross-chain BTC—issuing sBTC on the Stacks network—which amounts to a centralized mapping approach, introducing single points of centralization risk.
Additionally, its network gas is paid in its native token STX, not BTC. Miners must stake BTC to mine STX and earn transaction fees, while STX stakers earn Bitcoin rewards. This dual incentive structure can create hesitation among miners regarding participation.
As of writing, Stacks lags far behind popular Ethereum L2s like Arbitrum, which boasts around 200,000 daily active users. Both user engagement and capital inflows remain lukewarm.
RSK: A General-Purpose Smart Contract Platform Secured by Bitcoin
RSK (Rootstock) is a general-purpose smart contract platform secured by the Bitcoin network. By porting Ethereum smart contracts to RSK, it enables all Ethereum dApps to become compatible with the Bitcoin blockchain. With a new block created approximately every 33 seconds—much faster than Bitcoin’s 10-minute interval—and throughput of about 10–20 transactions per second (compared to Bitcoin’s ~5 TPS), RSK offers significantly higher efficiency.
What sets RSK apart from other Bitcoin layering solutions is merge mining. RSK uses the same Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus as Bitcoin, allowing miners to simultaneously secure both blockchains without additional computational cost. Through a process called merge mining, miners contribute hash power to both networks concurrently.
Because both chains share the same consensus mechanism, merge mining allows miners to validate transactions, generate blocks, and send them to Bitcoin, ensuring that RSK’s smart contracts benefit from Bitcoin’s robust security.
However, RSK relies on smartBTC (RBTC), a 1:1 pegged token backed by BTC locked on Bitcoin and bridged via vaults and smart contracts on RSK. This setup still exposes users to potential smart contract vulnerabilities on the RSK side.
BitVM: An Unproven Newcomer in Bitcoin Smart Contracts
BitVM aims to achieve Turing-complete Bitcoin contracts without modifying Bitcoin’s opcode. Its key innovations include:
-
Introducing state across different UTXOs or scripts using Bit Commitments.
-
Enabling verifiability through logic gates: Any faulty program execution within the virtual machine can be deconstructed and verified by provers, ensuring false claims can be quickly challenged and proven invalid.
-
Maintaining Bitcoin’s lightweight nature: Similar to Optimistic Rollups on Ethereum, BitVM avoids executing heavy computations on Bitcoin. Instead, it minimizes on-chain activity, only challenging incorrect executions. Only the output of BitVM programs appears in Bitcoin transactions, functioning more like solvers and validators.
Currently, BitVM’s capabilities are extremely limited and largely theoretical. Only one function—zero-check functions—is practically feasible today. Future use cases could include bidirectional pegging with sidechains for scalability, following a logic similar to Ethereum’s Rollup model:
Running fraud proofs akin to Optimistic Rollups (OPR) on BTC scripts. If a disputed asset transfer occurs, users can file a challenge. If wrongdoing is confirmed, the dishonest party’s assets are slashed. Valid challenges must typically occur within 7 days (analogous to a 7-day no-questions-asked return policy). Challenges filed after this window are invalid—even if the transaction was fraudulent, it becomes permanently recorded on-chain.
Moreover, BitVM’s smart contract layer runs off-chain, with each contract maintaining isolated states. Cross-chain BTC relies on traditional hash locks for asset anchoring, lacking true decentralized BTC bridging and failing to eliminate risks associated with centralized arbitration nodes.
BEVM: A Fully Decentralized Bitcoin L2 Solution
BEVM is a BTC-gas-powered, EVM-compatible Bitcoin Layer 2 designed to expand Bitcoin’s smart contract capabilities. Its core goal is to free BTC from the limitations of Bitcoin’s non-Turing-complete, smart-contract-incompatible base layer, enabling decentralized applications where BTC serves as the native gas on BEVM’s Layer 2.
When users bridge BTC from the Bitcoin mainnet to BEVM, their BTC is sent to a contract address managed by 1,000 nodes. Simultaneously, an equivalent amount of BTC is minted 1:1 on the BEVM (Bitcoin L2) network.
When users initiate a withdrawal back to the Bitcoin mainnet, BEVM network nodes trigger the Mast contract. The 1,000 custodial nodes automatically sign according to predefined rules, returning BTC to the user’s address—enabling fully decentralized, trustless cross-chain transfers.
This means all transactions are moved from Bitcoin’s main chain to the Layer 2 network. And because BEVM is fully EVM-compatible, developers can seamlessly deploy existing Ethereum dApps on BEVM, rapidly building DeFi applications such as swaps, lending, and liquid staking—greatly enriching the Bitcoin ecosystem. Compared to earlier options, BEVM offers the highest degree of decentralization and usability.
MAP Protocol: A Peer-to-Peer Interoperable Bitcoin L2 Network
MAP Protocol is a Bitcoin Layer 2 network enabling peer-to-peer cross-chain interoperability. It leverages Bitcoin’s security mechanisms to allow assets and users from other public chains to interact seamlessly with Bitcoin, enhancing overall network security and enabling BRC20 cross-chain functionality.
Compared to the Bitcoin main chain, MAP Protocol offers significantly lower Gas fees—potentially as low as 35% of costs on platforms like Unisat and OKX Ordinals.
By leveraging MAP Protocol’s Bitcoin L2 technology, users can trade BRC20 tokens with inscriptions at low Gas costs and zero congestion on platforms like SATSAT. They can also roll back transactions to the Bitcoin main chain via Rolluper, enabling trading on L1 platforms such as Unisat and OKX.
Conclusion
As the broader crypto community increasingly recognizes the importance of Layer 2 solutions in shaping Bitcoin’s future, the Bitcoin L2 sector stands poised for new growth opportunities. The build cycle will be long, making now an ideal time for early positioning.
Particularly promising are the most innovative L2 solutions and their derivative application scenarios—just as Arbitrum and Optimism did for Ethereum in 2021, a few Bitcoin L2 leaders are destined to emerge as billion-dollar projects.
Therefore, as a novel solution path, Bitcoin L2 opens vast new frontiers of possibility. Still in its blue-ocean infancy, it represents an untapped wealth opportunity worthy of long-term attention.
Hence, ETF approval remains the biggest catalyst in the current crypto market, offering substantial upside potential with limited downside risk. Despite some liquidity concerns, if investor appetite surges, ETFs could dramatically improve overall market conditions.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News












