Quantum Computing, AI, and DeFi: Preparing for a Technological Paradigm Shift
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

Quantum Computing, AI, and DeFi: Preparing for a Technological Paradigm Shift
Regardless of the future of quantum computing, it is bound to be an interesting and disruptive journey.
By Kava Labs
In our previous article on AI-driven risk assessment, we explored how AI enhances cybersecurity through anomaly detection and predictive analytics. But what if another independent, innovative technology emerged—triggering a new technological paradigm shift within decentralized finance (DeFi)? What if this new technology could completely undermine the cryptographic foundations upon which DeFi relies?

With the advancement of quantum computing, many experts are expressing concerns about its future implications. These concerns have existed since the early days of cryptocurrency—and even earlier, dating back to the inception of modern cryptography. However, they intensified significantly after Google announced in Q4 2024 its latest quantum computing chip, Willow.
Therefore, in this article, we will explore the principles of quantum computing, its potential threats to DeFi, and whether the industry should be vigilant moving forward.
Traditional Computing vs. Quantum Computing
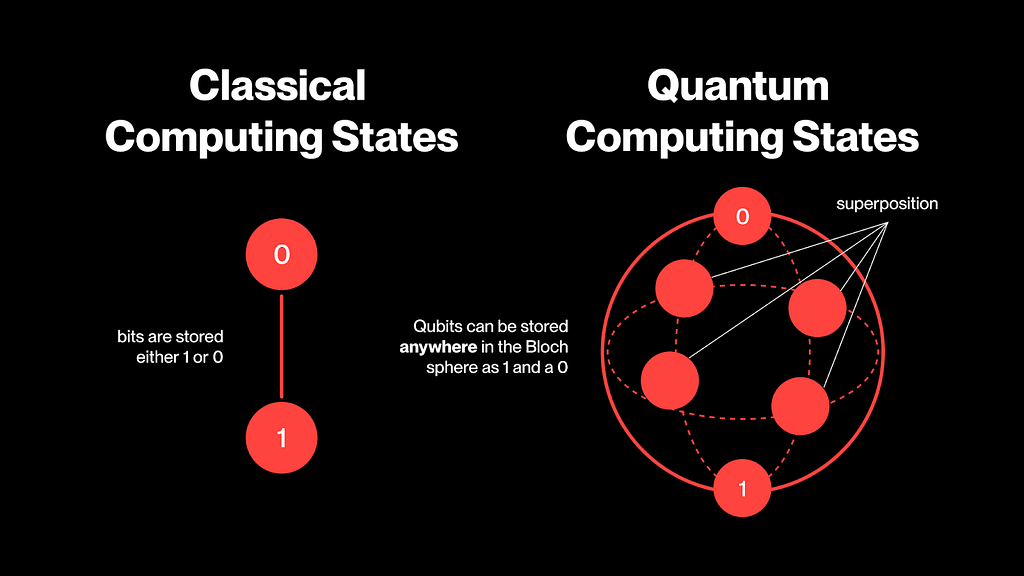
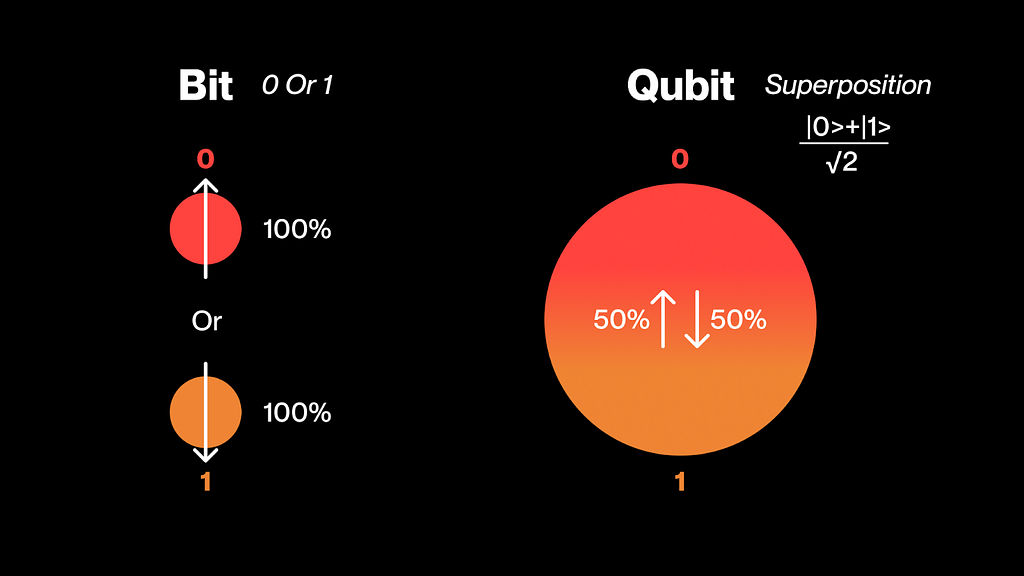
To understand the threat posed by quantum computing, it's essential first to recognize how fundamentally different it is from the traditional computing systems we use today. To begin understanding this difference, we must dive into the smallest unit of digital information—the bit. The bit has long served as the foundational building block of all modern computing technologies, historically represented as either a 0 or a 1.
This basic unit enables modern computing systems to build complex structures on top of a stable binary foundation. The strength of the binary system lies in providing a reliable base for constructing increasingly larger and more sophisticated systems.
Quantum computing challenges the very nature of this binary model by introducing an alternative form of computational unit. In quantum computing, the quantum bit—or qubit—not only exists in states analogous to classical bits but also allows for multiple simultaneous truths in terms of whether it encodes a 1 or a 0.
Superposition
Superposition is one of the core principles of quantum computing, yet it remains highly abstract and difficult for some to grasp. In classical computing, a bit’s state is always 100% certain—either 1 or 0. In contrast, a quantum bit (qubit) can represent both 1 and 0 simultaneously. Imagine something being both "yes" and "no" at the same time—a concept that defies logic under traditional thinking and classical models.
The simplest way to explain this phenomenon is through the work of 20th-century physicist Erwin Schrödinger and his theory on the uncertainty principle in quantum mechanics. You may be more familiar with Schrödinger's cat thought experiment: a cat is placed inside a sealed box containing a Geiger counter and a radioactive substance that, when decayed, releases poison. Theoretically, because the decay process is inherently uncertain, the cat exists in a state of being both alive and dead until the box is opened and observed. Similarly, a qubit remains in a dual state—both "alive" and "dead"—until forced into a definite outcome via measurement.
Entanglement
If you’re still reading, congratulations—your brain hasn’t short-circuited yet from grappling with quantum concepts. Now that we’ve covered what qubits are and how they function, let’s go deeper into how particles within each qubit relate to one another. This brings us to entanglement, the second cornerstone of quantum computing.
We've already seen how quantum computing operates using analogies like Schrödinger’s cat. But entanglement takes this analogy further. Quantum computing isn't just about maintaining two states at once; it involves multiple interconnected scenarios across different locations that influence each other. Think of navigating a maze. In classical computing, if your first path leads to a dead end, it gets marked as zero. A second failed attempt follows sequentially, continuing until the correct route is found. With quantum computing, however, all possible paths are mapped simultaneously—each failure and success influencing every other possibility in real time.

Thought Experiment or Reality?
Although grasping the theoretical underpinnings of quantum computing is extremely challenging, doing so is crucial if we are to appreciate the scale of innovation in computational power. The superposition and entanglement of qubits enable quantum computers to solve problems at speeds and scales far beyond anything conceivable with today’s technology.
In our article on the limits of technological innovation, we illustrated various sizes of digital data—from the kilobytes needed to store a five-page document to the megabytes required for a three-minute MP3 file. Understanding the magnitude of digital data helps clarify why replacing the fundamental building blocks from bits to qubits creates such a compounding effect.
With this framework in mind, we can start to appreciate the sheer power of quantum computing. Google claims its newly launched Willow quantum chip can solve a problem in five minutes that would take the fastest conventional computer on the market today ten billion trillion years (10^27 years). That’s five minutes versus 10,000,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 years—an incomprehensible gap.

The End of Modern Cryptography?
You might already see where this is going: quantum computing could pose a systemic threat to the DeFi industry. Such immense computational power could break the cryptographic security underpinning the entire blockchain ecosystem. Brute-force attacks could instantly reveal private keys and drain user accounts.
As previously discussed in our article on AI-blockchain interoperability, integration between artificial intelligence and blockchain could create a “poison pill” scenario exploited by malicious actors. Now, combining those theories with the potential of quantum computing, it’s easy to imagine a future where the entire DeFi space collapses within minutes.
Reasons for Optimism
If you're concerned about the threat quantum computing poses to DeFi, there are still several reasons to remain optimistic. First, if you haven’t realized it yet, quantum computing is incredibly complex, difficult, and expensive. Today, only a handful of quantum computers exist, mostly developed in tightly controlled environments by companies like IBM, Google, Amazon, and Alibaba. These organizations have no incentive to undermine DeFi’s cryptographic security—because doing so would also compromise the encryption protecting traditional banking systems and national defense infrastructures, including nuclear reactors and weapon systems.
Second, we often underestimate the relative size and importance of our industry. Currently, the total value locked (TVL) in DeFi stands at $125 billion. While significant, this remains a relatively small and young sector. Compare that to the money market banking sector, valued at over $909,647 billion, or the integrated oil and gas industry worth over $109 billion. As bleak as it may sound, if quantum computing advances rapidly and becomes a threat, attacking DeFi would be among the least attractive targets. The rest of the world—including much larger and more critical systems—would face equal or greater risks. Even if DeFi were targeted, society would face far more urgent consequences elsewhere—such as disruptions to global supply chains, AGI (Artificial General Intelligence), or nuclear weapon deployment. Securing DeFi and private keys may no longer be our top priority.
Moreover, as new threats emerge, so do new solutions. Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC) is now a major focus in the field. Developers are acutely aware of the dangers posed by unleashing quantum computing without adequate safeguards. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is leading global efforts to establish post-quantum encryption standards.
We should also view quantum computing as a positive force. The immense computational power offered by quantum models will drive unprecedented discoveries—from space exploration to global IoT networks and AI integration. Through our series, we’ve already seen how AI accelerates innovation in autonomous vehicles, medical breakthroughs, and drug discovery. Quantum computing will amplify and accelerate these advancements at a pace surpassing even the most optimistic futurists’ predictions.
Finally, we must acknowledge that quantum computing is still in its infancy. Even with the release of the Willow quantum chip, practical, real-world applications of quantum computers remain limited. For them to become fully operational and integrated into everyday life, extensive indexing of the current digital environment is necessary. Transitioning industries to resist quantum threats—or simply preparing to harness their benefits—will be a formidable challenge for society. Regardless of quantum computing’s trajectory, it promises to be a fascinating and disruptive journey. How DeFi, artificial intelligence, and post-quantum cryptography respond will define one of the most pivotal eras of the 21st century.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News