KYC-free instant exchange: Mixing alternatives beyond Tornado Cash
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

KYC-free instant exchange: Mixing alternatives beyond Tornado Cash
This article introduces what no-KYC instant exchange platforms are, their trading mechanisms, and how they are used in money laundering scenarios.
As is well known, after hackers exploit smart contracts to obtain substantial gains, most choose to deposit the funds into Tornado Cash for coin mixing. By breaking the link between deposit and withdrawal addresses, hackers can launder the money and eventually convert the cryptocurrency into cash. For users of Tornado Cash, the liquidity within the mixing pool determines how effectively they can obscure fund flows—especially when dealing with very large amounts. Following the August 2022 sanctions against Tornado Cash and the arrest of its founder Alexey, liquidity in Tornado Cash’s contracts sharply declined. At the same time, we observed a significant increase in traffic on alternative mixing channels on Ethereum, such as KYC-free instant swap exchanges like FixedFloat.
This article will explain what KYC-free instant swap exchanges are, how they operate, and how they are used in money laundering scenarios.
What Are KYC-Free Instant Swap Exchanges?
A KYC-free instant swap exchange is a cryptocurrency platform that enables users to instantly exchange digital assets without providing personal identification (Know Your Customer, or KYC). While these platforms were originally designed to serve on-chain traders, certain characteristics have led them to be frequently used as tools for coin mixing:
-
Anonymity: Transactions on these platforms require no personal information—users only need a blockchain address to conduct trades.
-
Cross-chain transactions: Users can trade assets across multiple blockchains, making fund flows harder to trace—particularly when the platform supports privacy coins like Monero or Zcash.
-
Limited compliance scrutiny: FixedFloat rarely freezes transaction funds because trades complete quickly, unless the stolen funds originate from a high-profile project such as Curve.
-
Instant swaps: The entire process is automated, with transactions typically completed within 20 minutes at the latest.
Transaction Mechanism
The user experience of these exchanges lies somewhere between centralized exchanges (CEX) and decentralized exchanges (DEX). Unlike CEXs, users do not need to deposit funds into an exchange-controlled wallet and wait for order book matching. Instead, they trade directly against the KYC-free exchange as counterparty, eliminating separate deposit and withdrawal steps. Unlike DEXs, trades are not executed via smart contracts but through backend systems operated by the exchange.
Below we use FixedFloat’s transaction flow as an example:
1. On the homepage, users select the desired cryptocurrency pair and amount to exchange. There is a per-transaction upper limit, determined by the platform’s available liquidity for that token—but a single address can perform unlimited transactions.
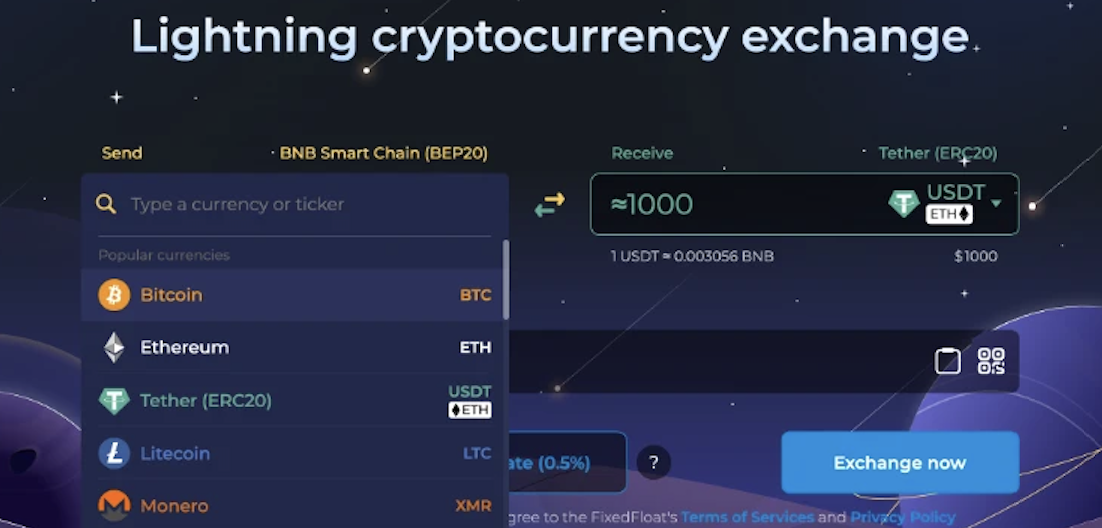
2. Users specify the receiving address and order type. FixedFloat offers two types: fixed-rate and floating-rate orders. A fixed-rate order incurs a flat 1% fee plus network costs, shielding the user from minor price fluctuations during processing. A floating-rate order has a lower 0.5% fee plus network costs but exposes the user to potential slippage due to market movements.
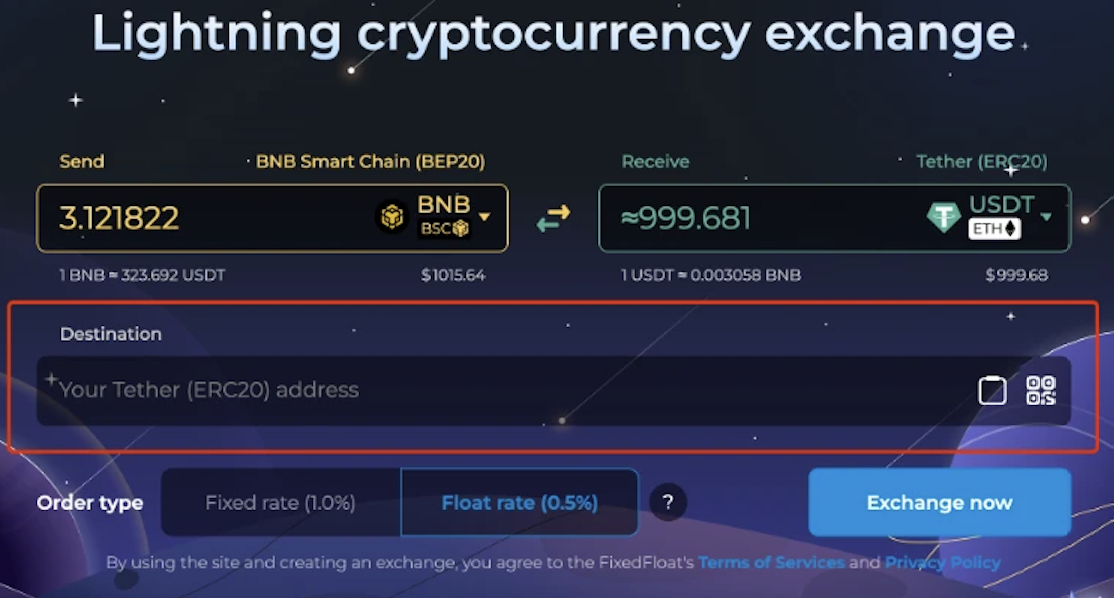
3. After initiating the trade, FixedFloat generates a new deposit wallet. The user must send funds to this designated address within a specified timeframe. After several block confirmations, the platform sends equivalent funds from its hot wallet to the user’s designated receiving address, completing the transaction.
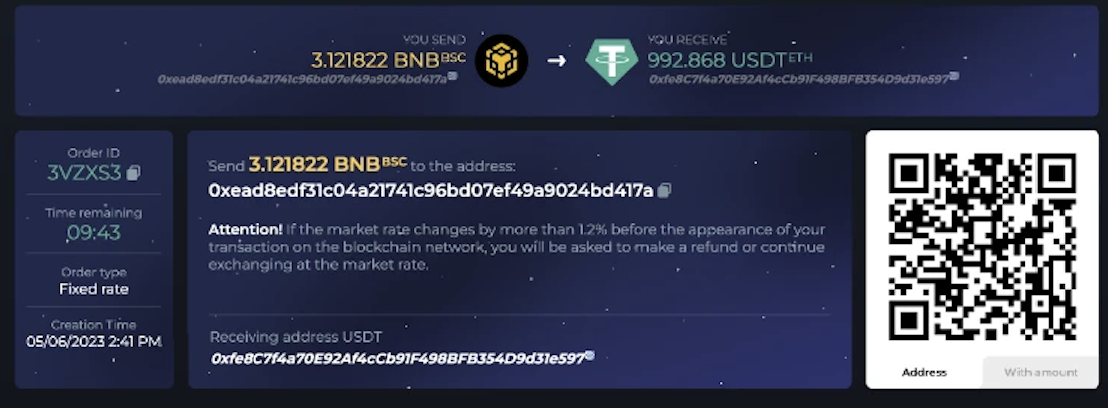
As previously mentioned, each transaction is subject to size limits based on platform-imposed caps and the liquidity available in the exchange’s hot wallet. When liquidity for a particular token runs low, the platform typically replenishes it via centralized exchanges such as Binance.
Most KYC-free exchanges follow similar processes, though some optimize specific steps. For instance, SideShift.ai uses smart contract addresses for all ERC-20 deposit wallets. When users send ERC-20 tokens to these contract addresses, the platform does not need to separately send ETH to cover gas fees for transferring tokens to its hot wallet. Instead, it can directly call the contract’s Flush method to aggregate the tokens.
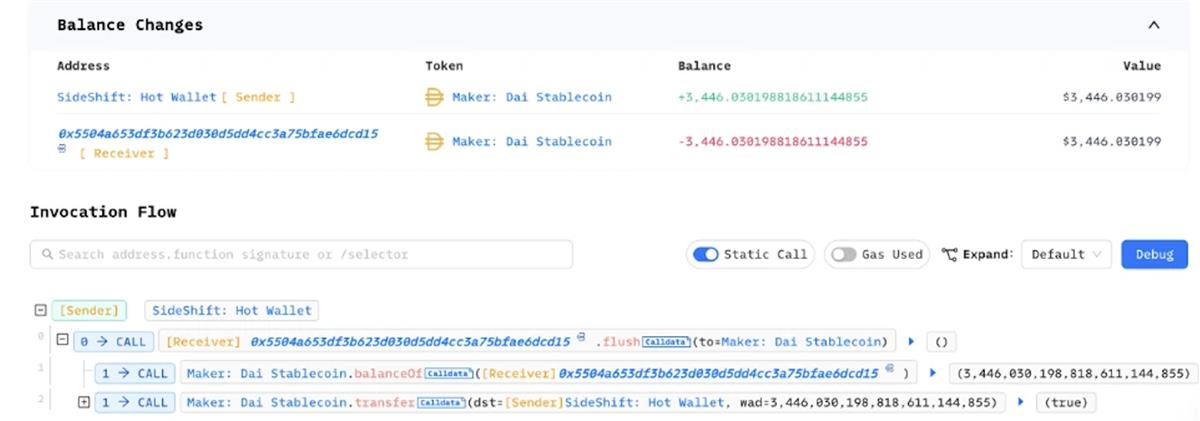
On-Chain Data Analysis
We conducted on-chain behavioral analysis of three widely used KYC-free instant swap exchanges—FixedFloat, ChangeNow, and SideShift—and compared them with Tornado Cash.
In terms of Ethereum traffic share, Tornado Cash was overwhelmingly dominant among these channels before being sanctioned. However, following the sanctions in August last year, its traffic share plummeted. Since then, FixedFloat and ChangeNow have taken the lead, collectively accounting for around 80% of traffic in most recent periods. Nevertheless, whenever large-scale thefts occur, hackers still tend to prefer Tornado Cash for laundering. This indicates that while the number of users on KYC-free instant swap exchanges far exceeds that of Tornado Cash, individual deposits on Tornado Cash remain significantly larger than those on other platforms.
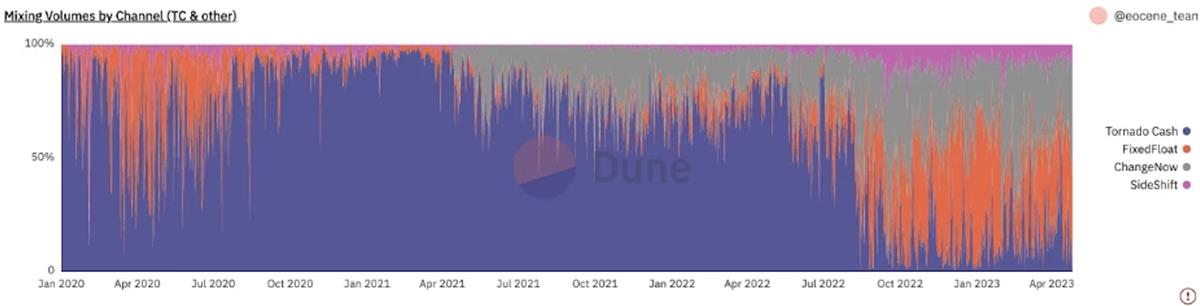
Use of KYC-Free Exchanges in Fund Obfuscation Scenarios
1. Direct Use as Mixing Channels
Like Tornado Cash, KYC-free exchanges can be directly used for money laundering. For example, in the Curve hack of August 2022, the hacker used FixedFloat and SideShift to move stolen funds. According to analysis by the Eocene team, the hacker bridged the funds to other chains, making subsequent tracking extremely difficult.
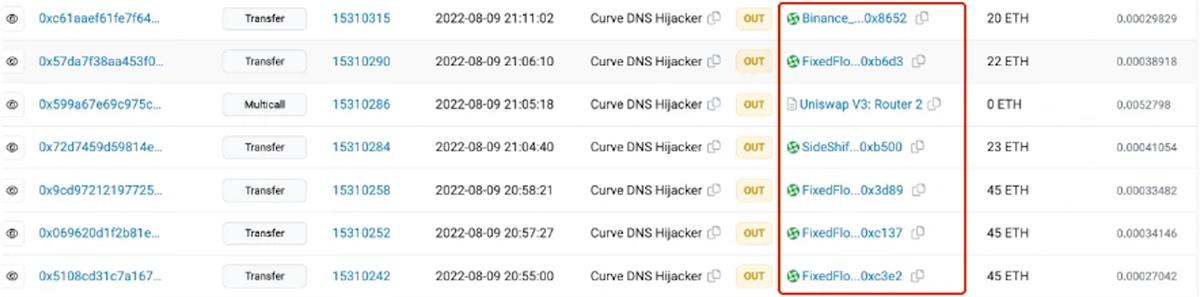
2. Use as Source of Attack Funding
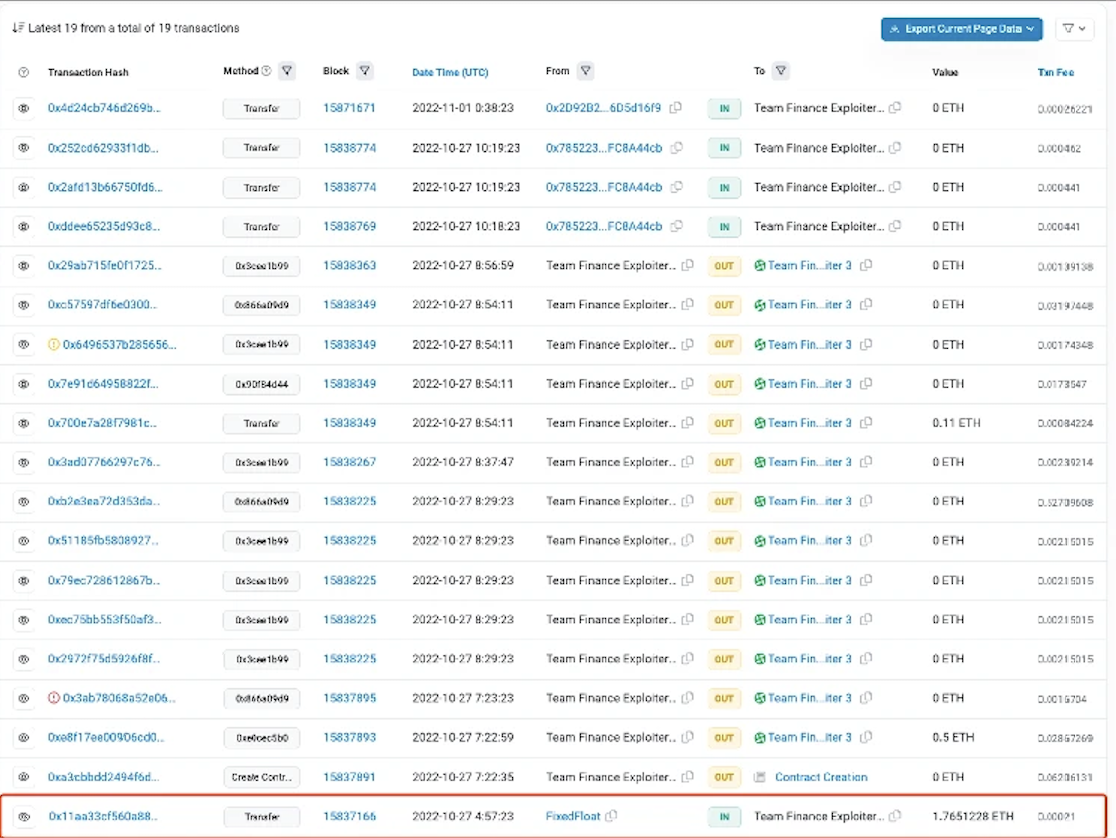
The source of funding for hacker attacks is often a crucial clue in fund tracing. We can sometimes gain insights by tracing back the origin of gas fees paid by attacker addresses. However, some hackers use KYC-free exchanges to send gas fees to their attack addresses, complicating tracking efforts. For example, in the Team Finance hack, the attacker used FixedFloat to provide initial funds to the attack address.
3. Combined Use with Other Mixing Tools
We have observed certain on-chain addresses combining multiple mixing tools to enhance fund obfuscation. For example, many addresses withdrawing from Tornado Cash subsequently route the withdrawn ETH through KYC-free exchanges like FixedFloat. Such sequential use of mixing tools presents additional challenges for fund tracing. The image below shows an address that withdrew 100 ETH from Tornado Cash and later transferred all funds via FixedFloat.
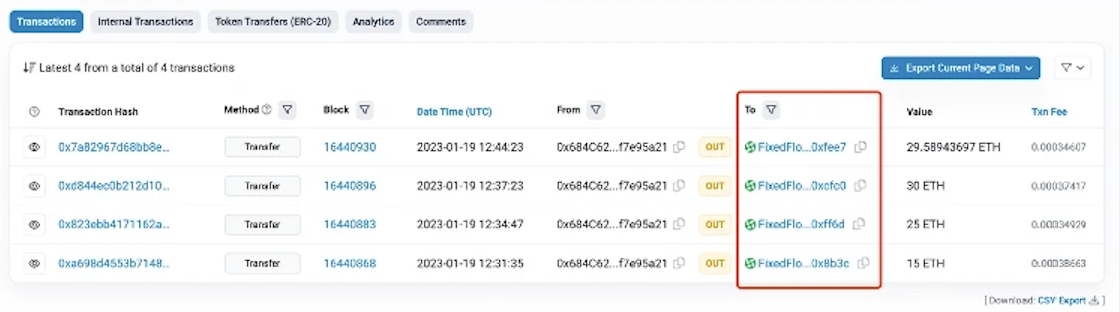
Tracking Funds Through KYC-Free Instant Swap Exchanges
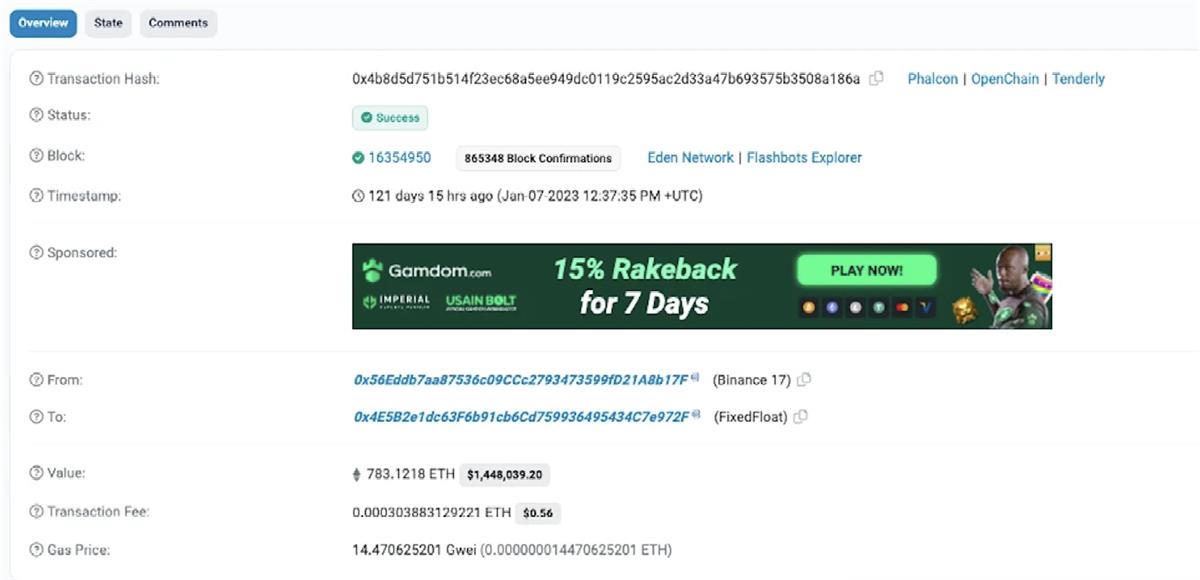
From an on-chain data perspective, transaction behavior on KYC-free exchanges closely resembles that of CEXs: both assign deposit addresses and maintain one or more hot wallets to receive user funds. For example, FixedFloat’s Ethereum hot wallet address is 0x4e5b2e1dc63f6b91cb6cd759936495434c7e972f.
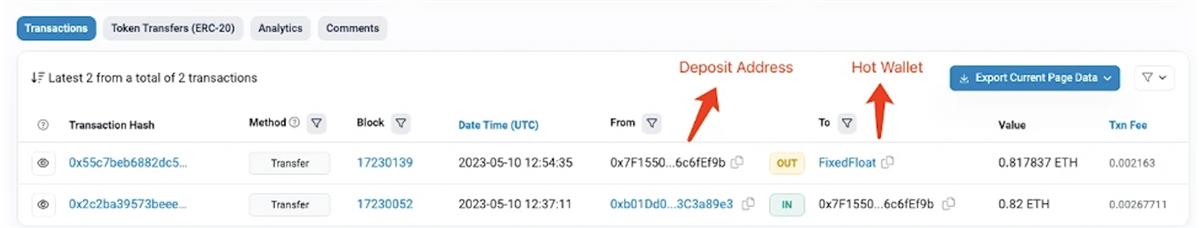
Unlike CEXs, where internal transactions are opaque black boxes, all transactions conducted through KYC-free instant swap exchanges are recorded on-chain—providing opportunities for fund tracing. By analyzing data across multiple chains and examining transaction amounts, the Eocene team has already been able to trace the sources of 50% of withdrawal transactions from FixedFloat’s Ethereum operations. With this information, investigators can gather more intelligence during fund tracking to locate the ultimate destination of illicit funds. If you need assistance tracing the downstream flow of funds that entered FixedFloat, please contact us via email or Twitter.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News
















