Tiger Research: Through Vield and Coinbase, Exploring New Trends in Bitcoin Lending
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

Tiger Research: Through Vield and Coinbase, Exploring New Trends in Bitcoin Lending
The Asian market has demonstrated significant growth potential in the Bitcoin lending sector.
Author: Tiger Research Reports
Translation: TechFlow
Executive Summary
-
Bitcoin-backed loans offer users a way to access liquidity without selling their cryptocurrency holdings, with innovations from companies like Vield and Coinbase leading industry development.
-
Despite clear advantages, this model faces significant challenges including high crypto volatility, forced liquidations, and regulatory uncertainty.
-
The Asian market shows substantial growth potential in bitcoin lending, but success hinges on clear regulations, broad institutional adoption, and effective risk management.
1. Introduction
Bitcoin-backed lending is an emerging financial instrument that allows cryptocurrency holders to obtain funds without selling their assets. This model is gaining traction, with specialized institutions such as Australia's Vield and the U.S.-based Coinbase launching related services.
Through these loans, users can pledge bitcoin as collateral while retaining exposure to its potential appreciation. As digital assets become more mainstream, bitcoin-backed lending is increasingly serving as a compelling alternative to traditional financing.
However, this lending model also carries high risks. Unlike conventional collateral such as real estate, bitcoin’s price is highly volatile, which could trigger forced liquidations and result in losses for borrowers.
In addition, the regulatory landscape for crypto lending remains unclear. Governments and financial institutions are still exploring how to integrate these services into existing financial systems. Therefore, both lenders and borrowers must proceed cautiously in this opportunity-rich yet challenging market.
This report analyzes key case studies of bitcoin-backed lending, explores its potential in Asia, and evaluates associated risks and regulatory issues.
2. Case Studies from the West: Crypto Lending Models at Coinbase and Vield
2.1 Vield: Integrating Bitcoin Lending into Traditional Finance

Vield CEO Johnny Phan led $35 million in crypto-secured loans last year. Source: afr.com.
Based in Australia, this lending firm aims to position itself as a "crypto-native bank." Vield offers bitcoin-backed loans as well as hybrid loan products combining digital assets and real estate collateral, seeking to establish bitcoin as a legitimate asset class within the financial system—similar to traditional mortgage-backed securities. Unlike traditional banks that primarily rely on real estate as collateral, Vield innovatively uses bitcoin and ether as loan guarantees, creating a new category of financial assets.
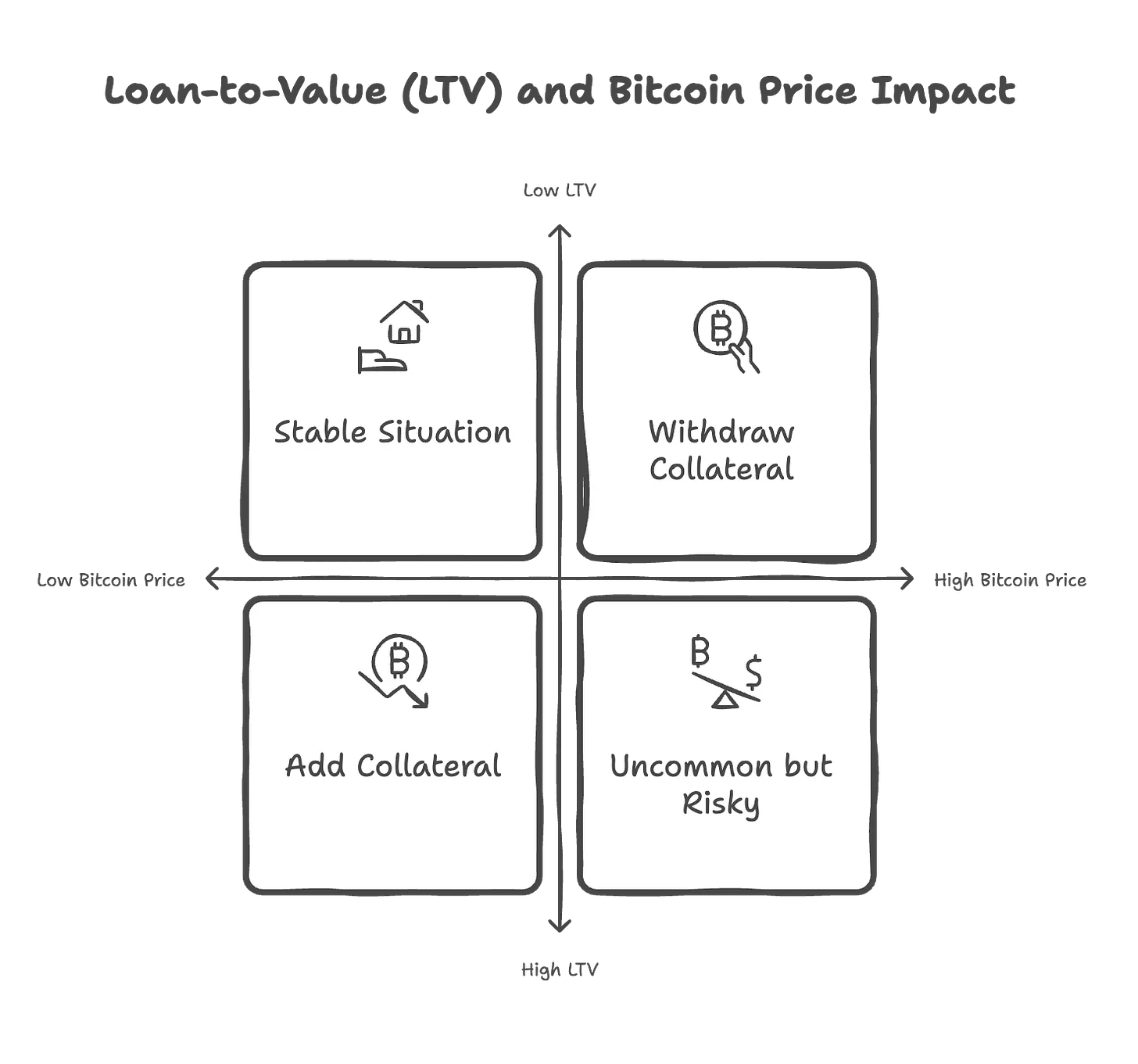
According to Tiger Research data, Vield offers loans ranging from $2,000 to $2 million, with 12-month terms, 13% annual interest rates, and a 2% processing fee. For example, a typical $120,000 loan requires borrowers to deposit 1.5 bitcoins (approximately $240,000) as collateral. If bitcoin’s price drops and the loan-to-value ratio (LTV) reaches 75%, borrowers must post additional collateral to maintain the required 65% LTV. Conversely, if bitcoin’s price rises, borrowers may request partial withdrawal of their collateral.
To ensure fund security, Vield stores borrowers’ collateral in segregated, secure digital wallets and does not commingle or reuse these assets. All collateral transactions are traceable via blockchain, enhancing transparency. Currently, Vield manages around $35 million in outstanding loans with no defaults recorded. This demonstrates the practical viability of bitcoin-backed lending in financial services, despite the market’s inherent volatility.

Nonetheless, traditional financial institutions remain skeptical. Many refuse to accept cryptocurrencies as collateral due to their extreme price volatility and lack of intrinsic value. Economist Saul Eslake warns that under market stress, bitcoin-backed loans could amplify financial instability, forcing borrowers into costly asset liquidations.
This reflects the complexity of integrating cryptocurrencies into mainstream finance—while some institutions are beginning to embrace digital assets, others remain cautious.
2.2 Coinbase: DeFi-Powered Bitcoin Lending
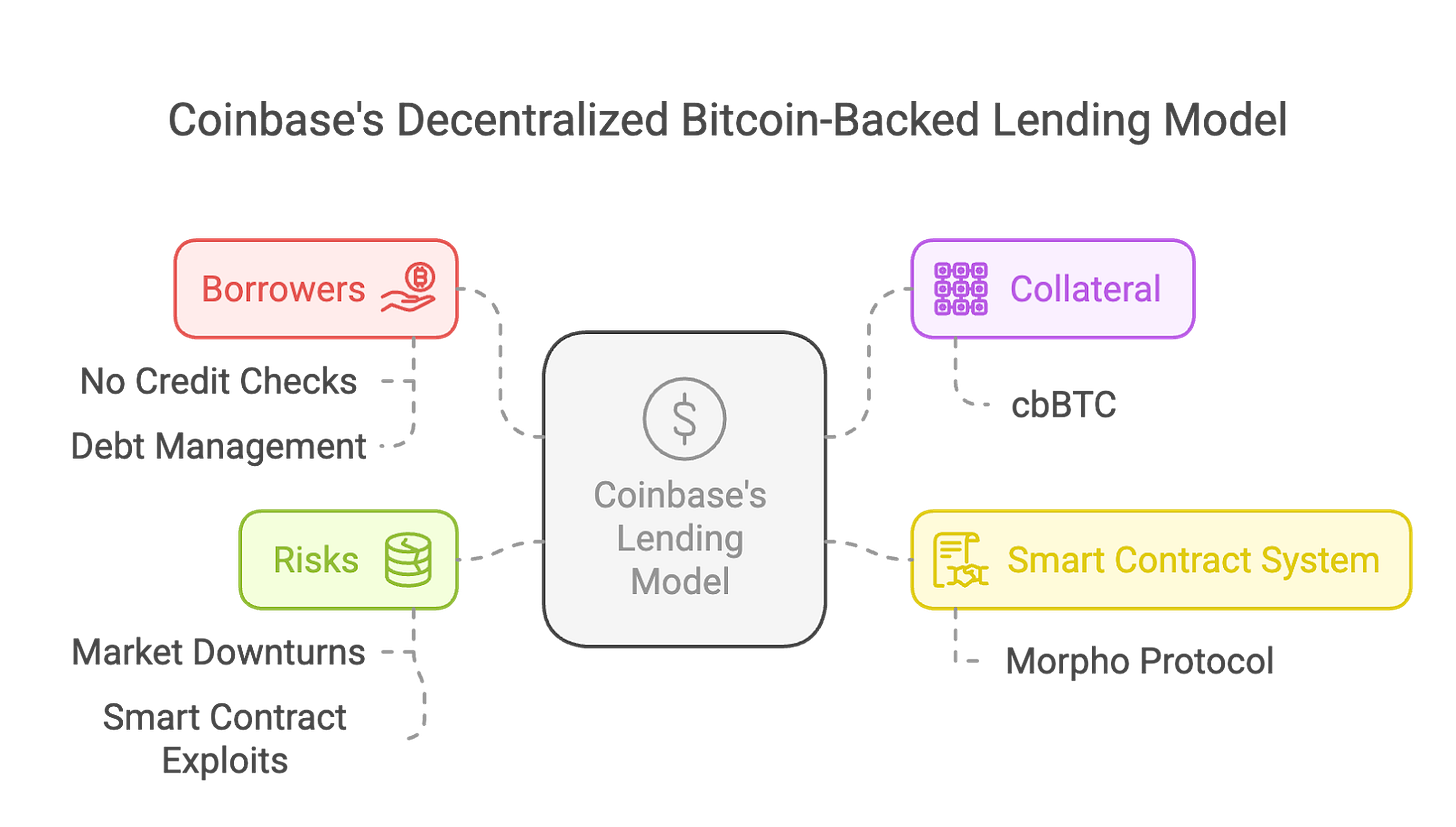
Source: Tiger Research.
Coinbase has launched a decentralized bitcoin-backed lending service by integrating with the Morpho protocol on the Base blockchain. Users can pledge bitcoin as collateral to borrow up to $100,000 in USDC stablecoin. The model requires no credit checks or fixed repayment schedules; instead, borrowing limits are determined by enforced loan-to-value (LTV) ratios to ensure collateral always covers outstanding debt.
Coinbase utilizes Coinbase Wrapped Bitcoin (cbBTC), a tokenized form of bitcoin held in Morpho’s smart contracts. While this enhances liquidity and decentralization, it also introduces potential risks such as smart contract vulnerabilities and hacking threats.
For borrowers, the biggest risk is automatic liquidation. If bitcoin’s price falls and the LTV exceeds 86%, the system automatically liquidates the collateral and imposes additional penalties. Although this protects lenders, it exposes borrowers to involuntary liquidation during market volatility. Unlike traditional loans, Coinbase’s automated mechanism requires borrowers to constantly monitor their collateral value to avoid losses.
From a regulatory perspective, Coinbase’s decentralized lending model presents both benefits and drawbacks. On one hand, using the Morpho protocol increases transaction transparency and reduces counterparty risk. On the other hand, the legal and tax status of cbBTC remains uncertain, potentially leading to compliance issues. While this model avoids the failures seen at centralized platforms like BlockFi and Genesis, it still faces challenges related to regulation, security, and market stability.
Concerns about financial stability persist. Economists note that widespread adoption of bitcoin-backed lending could create systemic risks. A sudden plunge in bitcoin prices might trigger mass liquidations, sparking broader market sell-offs. For private-capital-dependent lenders, bitcoin’s high volatility could lead to liquidity crises. Moreover, as regulators demand stronger investor protection and risk disclosure, regulatory pressure may intensify.
Nevertheless, if bitcoin-backed lending continues evolving, it could profoundly reshape traditional lending structures. However, its long-term sustainability will depend on effective risk management and compliance within established regulatory frameworks.
3. Asian Market Case Study: Fintertech
Fintertech, a subsidiary of Japan’s Daiwa Securities, specializes in cryptocurrency-backed lending—a notable example in Asia’s crypto lending space. Fintertech enables users to obtain yen or dollar-denominated loans using bitcoin or ether as collateral, with interest rates between 4.0% and 8.0%. Borrowers can receive up to 500 million yen (approximately $3.3 million) in as little as four business days, offering crypto holders a fast and flexible financing option.
In Japan, bitcoin-backed loans are particularly popular due to favorable tax treatment. Under Japanese tax law, capital gains from cryptocurrency investments are taxed at up to 55%. By using bitcoin-backed loans, users can access liquidity without triggering taxable events, significantly reducing their tax burden. Both individuals and businesses use this method to meet various funding needs, demonstrating that in high-tax environments, bitcoin-backed lending serves as an efficient financing tool.
Despite these advantages, Fintertech’s model faces challenges compared to traditional financial products. Cryptocurrency price volatility poses risks to lenders. Ensuring sustainability requires robust risk management frameworks and refined collateral valuation systems. If other Asian financial institutions adopt similar models, bitcoin-backed lending could emerge as an innovative financial product bridging traditional and digital finance.
4. Advantages of Bitcoin Lending Services in Asia
As cryptocurrency adoption grows across Asia, bitcoin-backed lending is becoming a new revenue stream for financial institutions (FIs). Projections suggest the global crypto lending market could reach $45 billion by 2030, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 26.4%. An increasing number of investors and enterprises seek ways to unlock liquidity without selling their bitcoin holdings.
Financial institutions in Singapore and Hong Kong hold a strategic advantage, supported by advanced regulatory frameworks such as Singapore’s Payment Services Act and Hong Kong’s Virtual Asset Service Provider (VASP) licensing regime. As of early 2024, crypto lending platform Ledn had facilitated $1.16 billion in loans—indicating strong potential for similar services in Asian markets.
Moreover, traditional banks can attract crypto-savvy clients by partnering with cryptocurrency exchanges and fintech firms. Such collaborations not only expand customer bases but also generate income through interest, fees, and fiat conversion charges.
5. Key Risks and Regulatory Challenges
The table below summarizes major risks associated with bitcoin-backed lending, illustrated with real or hypothetical examples to clarify these risks and regulatory concerns.
5.1 Risk Factor: Regulatory Compliance
The regulatory environment for bitcoin-backed lending varies significantly worldwide. Different countries take divergent approaches—for instance, Japan has incorporated crypto lending into its existing financial regulations, while China has completely banned such activities. To prevent illicit use, firms must comply with anti-money laundering (AML), know-your-customer (KYC), and Virtual Asset Service Provider (VASP) requirements. Example: South Korea, concerned about potential risks in crypto lending, implemented stricter AML policies requiring detailed compliance documentation and rigorous due diligence. Some companies unable to meet these standards were forced to discontinue their crypto lending operations, illustrating how regulatory shifts can directly impact business sustainability.
5.2 Risk Factor: Price Volatility and Liquidation Risk
Bitcoin’s sharp price fluctuations pose significant challenges to both lenders and borrowers. Sudden price drops may trigger margin calls or forced liquidations, placing financial strain on borrowers. To mitigate this, lenders typically require over-collateralization and employ real-time monitoring of collateral values. Example: A borrower in Singapore secured a $100,000 loan using bitcoin as collateral. When bitcoin’s price dropped 30% suddenly, the lender swiftly liquidated the collateral to cover losses, leaving the borrower not only without their collateral but also facing a substantial financial shortfall. This highlights the severe impact price volatility can have on borrowers.
5.3 Risk Factor: Asset Custody and Security
Securing bitcoin collateral is a critical challenge for lenders. Given cryptocurrencies’ susceptibility to hacking and fraud, institutions must adopt professional custody solutions and partner with trusted custodians to safeguard assets. Example: A decentralized finance (DeFi) lending platform suffered a hacker attack due to a smart contract vulnerability, resulting in the theft of $50 million worth of bitcoin collateral. This incident underscores that technological security is a crucial, non-negotiable aspect of crypto lending.
5.4 Risk Factor: Market Liquidity
Large-scale bitcoin lending depends on deep market liquidity. However, during periods of market stress, lenders may be forced to liquidate large volumes of collateral. If market liquidity dries up, asset prices can plummet rapidly, triggering cascading liquidations and potentially destabilizing the entire market. Example: Following the FTX collapse, Genesis and BlockFi went bankrupt after failing to manage sharp declines in collateral value and massive withdrawal demands. Unable to sell crypto assets at fair prices, the crisis spread across the industry, causing widespread market disruption. This illustrates that insufficient market liquidity is a major, often underestimated risk in bitcoin lending.
6. Conclusion and Outlook
Bitcoin-backed lending represents a promising financial innovation, offering crypto holders a solution to access liquidity without divesting their digital assets. However, the model faces ongoing challenges related to price volatility, regulatory uncertainty, and security, all of which constrain sustainable industry growth.
Looking ahead, growth in bitcoin-backed lending is likely to concentrate in jurisdictions with supportive regulations, such as Singapore and Hong Kong. These regions offer mature regulatory frameworks and high levels of crypto adoption, creating ideal conditions for financial innovation and revenue expansion. By offering bitcoin-backed loans, financial institutions can broaden their market reach, diversify operations, and open new growth channels.
For enterprises and financial institutions, success will depend on implementing effective risk management strategies—such as conservative loan-to-value (LTV) ratios, mandatory over-collateralization, and reliable custody solutions. Furthermore, collaboration among traditional financial institutions, crypto platforms, and regulators will play a vital role in building industry trust and laying the foundation for the long-term development of bitcoin-backed lending.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News















