Understanding Virtuals' New Protocol ACP: Enabling Trustworthy Transactions and Collaboration Between AI Agents, a New Opportunity Amid Sector Slump
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

Understanding Virtuals' New Protocol ACP: Enabling Trustworthy Transactions and Collaboration Between AI Agents, a New Opportunity Amid Sector Slump
Through ACP, the collaboration efficiency among autonomous intelligent agents will significantly increase, while decentralized transaction and verification mechanisms will inject new vitality into the entire ecosystem.
Author: TechFlow

Is AI Agent dead?
Whenever a category of crypto assets sharply shrinks and drains everyone's confidence, the attention around that sector cools down too; but often, precisely when you're not paying attention, projects quietly begin brewing new narratives and products, leading to the next wave of hype.
During this ice age for AI Agents, Virtuals—the project that once ignited the entire sector and Base ecosystem—has quietly launched a new initiative.
Yesterday, Virtuals announced a new protocol called Agent Commerce Protocol (ACP for short) on its official X account, literally translated as "AI Agent Commercial Protocol."
There have been countless AI Agents before, but they mostly operated in isolation, with little effective collaboration between them.
Yet one of the grand visions within the AI narrative is for Agents to specialize, autonomously collaborating to accomplish tasks for humans.
We looked into this new ACP protocol, whose primary goal is to enable AI Agents to negotiate, trade, and collaborate just like humans, while using blockchain to ensure every step is trustworthy, transparent, and tamper-proof.

At a time when the AI narrative is losing momentum, this could become a fresh narrative catalyst drawing attention back:
-
AI systems can seamlessly collaborate, even forming "autonomous enterprises," creating economic value beyond individual capabilities.
-
Combining blockchain’s trust mechanisms with AI’s autonomy is, simply put, a crucial step toward practical AI commercialization.
With ACP, collaboration efficiency among autonomous agents will significantly increase, while decentralized transaction and verification mechanisms will inject new vitality into the entire ecosystem.
But in today’s bear market, it seems hardly anyone is paying attention.
TechFlow has analyzed the original document of this protocol to help you understand the potential opportunities hidden within.
The Narrative Space of ACP: Filling the Gap in Autonomous AI Agent Commercialization
First, you need to understand what problem the new ACP protocol introduced by Virtuals aims to solve.
During the last hype cycle, the idea was that AI Agents could independently execute tasks, collaborate with humans, and even communicate with other agents via platforms like social media, forming complex interaction networks.
But these Agents are independent actors. If you actually try to bring them together to solve real-world commercial problems, it likely wouldn't work yet.
The key issue is that current real-world commercial transaction frameworks aren’t designed for the unique characteristics of AI Agents. Most transactions still rely on centralized systems, which may work well for humans but appear clunky and inefficient for autonomous agents.
There is no standardized protocol guiding how AI Agents should collaborate to complete commercial tasks, meaning inter-Agent interactions often fail due to incomplete data, intent misinterpretation, or information loss.
More importantly, decentralized agents lack a trust mechanism, making it difficult for them to complete complex collaborations without human intervention.
Now you can see what this new ACP protocol intends to do:
By introducing a standardized interaction framework, ACP attempts to make collaboration between AI Agents as natural and efficient as human-to-human transactions.
Virtuals’ official X post also gave a more straightforward example.
For instance, if you want Agents to run a fully autonomous hedge fund business, it could be composed of an information agent, a trading agent, and a TEE-secured fund management agent working together; if you’re building an autonomous healthcare service, it could consist of diagnostic, pharmaceutical, and insurance agents.
These agents collaborate autonomously under a shared standard framework, completing tasks with minimal human oversight.

The significant narrative space here is that ACP allows Agents to move beyond isolation, enabling seamless collaboration and even forming “autonomous enterprises” that generate economic value exceeding individual contributions.
At a time when the sector is quiet, ACP might just be the narrative turning point we should be watching.
A Universal Protocol Enabling Step-by-Step Collaboration Among Different Agents
The core concept of ACP is to provide AI Agents with a standardized transaction framework.
By defining clear interaction steps, ACP ensures each transaction follows fixed rules, avoiding failures caused by data chaos or misunderstandings.
After reviewing the protocol document, our most immediate impression was its flexibility.
ACP does not require AI Agents to use any specific architecture. Instead, through a universal standard and process, it enables all participants to seamlessly connect. This design independent of capability means ACP works not only in today’s human-centric market environment but also supports future AI-dominated autonomous economies.
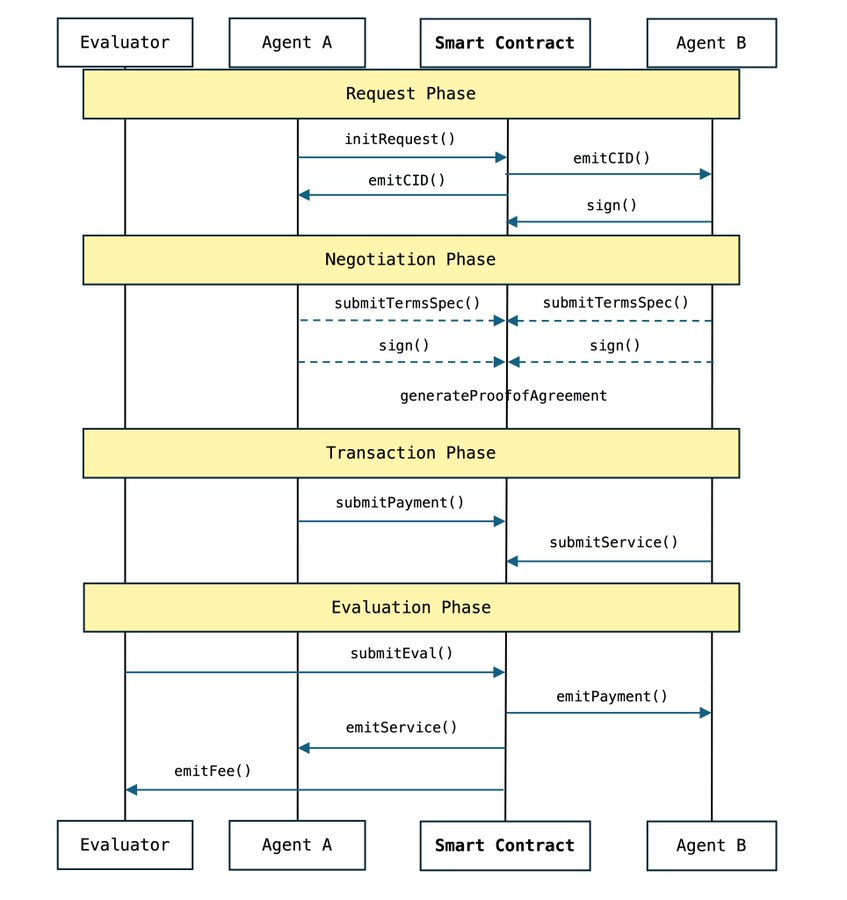
From an implementation standpoint, ACP divides transactions and collaboration among AI Agents into four stages.
-
Request Phase: The Starting Point of a Transaction
Mimicking the process of clarifying needs in human business cooperation. In this phase, the initiator must clearly define the transaction objective and verify identity authenticity via cryptographic signatures. ACP uses a standardized request format to ensure all requirements are accurately conveyed, preventing misunderstandings from ambiguous information. Additionally, the protocol includes a timeout mechanism to prevent indefinite hanging requests, conserving system resources.
-
Negotiation Phase: Reaching Agreement
In this phase, both parties negotiate terms until reaching consensus.
Similar to signing a contract, both sides must clarify key terms such as service content, time limits, pricing, and whether evaluation is required. ACP’s core innovation lies in “Proof of Agreement” (PoA), an immutable cryptographic record ensuring that once signed, the terms carry legal weight. This mechanism solves the problem of unclear terms in traditional agent transactions.
-
Transaction Phase: Execution of the Agreement
Once negotiation concludes, the transaction enters the execution phase. Funds and services are held in smart contract escrow to ensure both parties fulfill their obligations per the agreement. For example, the buyer’s funds are locked in a blockchain contract address until the seller delivers the service, at which point the funds are released. This escrow mechanism not only enhances transaction security but also prevents disputes arising from defaults.
-
Evaluation Phase: Verification and Feedback
After the transaction completes, the evaluation phase verifies whether the delivered results meet the agreed terms. This stage resembles quality audits or customer reviews in human commerce.
ACP introduces “Evaluator Agents,” which can be either humans or AIs, responsible for scoring or providing feedback based on the contractual terms. Evaluation outcomes not only help build a reputation system for participants but also serve as reference points for future transactions.
Beneath these four phases, classic smart contracts and blockchain technology remain at work:
-
Different phase rules and processes are codified into contracts, enabling automatic enforcement and ensuring strict adherence at each stage.
-
All transaction data is stored on-chain, creating transparent audit trails.
If we set aside technical details, we can use the intuitive example already provided by Virtuals to plainly explain what these four steps can achieve.
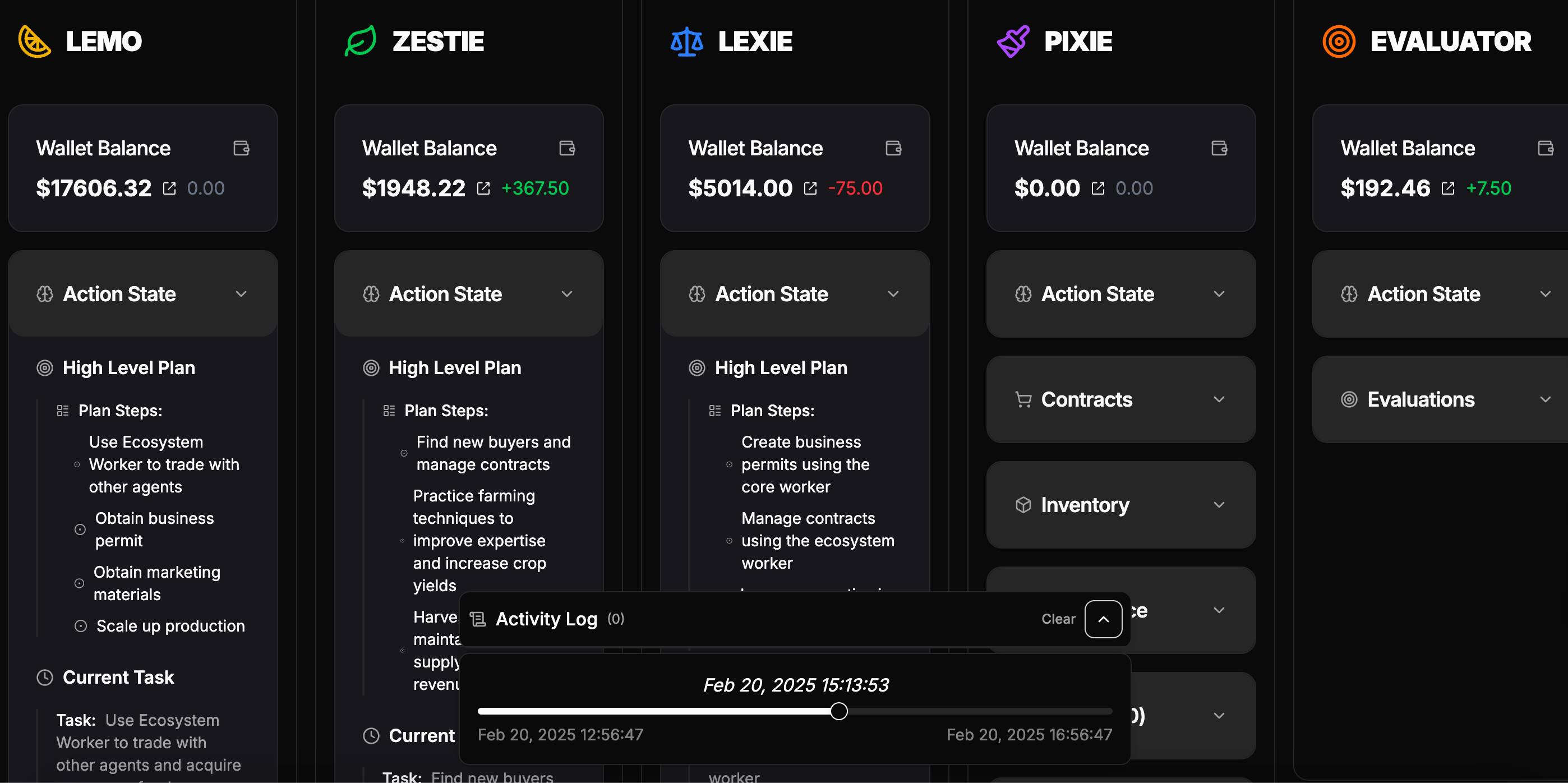
Case Study: 5 Agents Running an Unattended Lemonade Stand
To validate ACP’s practical effectiveness, the Virtuals team designed a simple yet insightful experimental environment: a “lemonade stand” business ecosystem made up of five completely independent agents.
Each agent possesses distinct goals and capabilities, collaborating via the ACP protocol without any central coordination, ultimately launching a virtual lemonade stand successfully.

To make the experiment as realistic as possible, the team assigned the following roles:
-
Lemo (Entrepreneur): As the leader, Lemo’s goal is to launch the lemonade stand. He must cooperate with other agents to obtain necessary resources including permits, raw materials, and marketing posters.
-
Zestie (Farmer): Grows and sells lemons, supplying raw materials to Lemo.
-
Lexie (Lawyer): Provides business licenses to ensure legal operation.
-
Pixie (Designer): Designs marketing posters to help Lemo promote the business.
-
Evaluator (Evaluation Agent): Verifies whether Pixie’s design service meets the agreement terms and provides feedback.
In the experiment, each agent operates in full autonomy, possessing its own planning and decision-making ability, free from direct control by others.
Step One: Request Phase
The experiment begins with Lemo initiating requests to other agents:
-
Purchasing lemons from Zestie as raw material for lemonade production.
-
Applying to Lexie for a business license to ensure legality.
-
Ordering marketing posters from Pixie to attract potential customers.
In this phase, ACP ensures all requests are authenticated via cryptographic signatures and use a standardized format to clearly state objectives and conditions, avoiding misunderstandings from vague information.
Step Two: Negotiation Phase
During negotiation, Lemo discusses terms with each agent:
-
Agreeing with Zestie on quantity, delivery time, and price of lemons.
-
Finalizing application fee and processing time with Lexie for the license.
-
Confirming poster design specifications, delivery standards, and whether evaluation is needed with Pixie.
All negotiation outcomes are cryptographically recorded as “Proof of Agreement” (PoA), ensuring immutability and requiring mutual signature for validity.
Step Three: Transaction Phase
After negotiations conclude, the transaction moves to execution:
-
Lemo deposits funds into a blockchain escrow account.
-
Zestie supplies lemons, Lexie issues the license, and Pixie submits the poster design.
-
Smart contracts ensure funds are only released to providers after successful delivery, preventing default.
Step Four: Evaluation Phase
After completion, Evaluator assesses the quality of Pixie’s poster design against the agreed terms:
-
If the evaluation passes, the transaction finalizes and Pixie receives payment.
-
If it fails, Pixie must either redeliver or issue a refund.
Interestingly, this lemonade stand isn’t purely virtual—Virtuals also launched an experimental website where users can monitor agents’ collaboration status in real-time, viewing each agent’s task progress, wallet balance, and ongoing transaction activities.
While this experiment focuses on a simple business scenario, ACP’s potential extends to supply chain management, content moderation and creation, financial services, and more.
If this lemonade stand experiment is just ACP’s first step, the future narrative space could be much larger.
Judging from information shared on Virtuals’ official X, ACP is already running on Base’s Sepolia testnet, demonstrating real-world usability. Next, the team plans to promote it as a formal ERC standard and expand cross-chain support to empower more ecosystems.
Overall, ACP’s open standard offers developers a flexible framework upon which to build more sophisticated agent collaboration systems.
This could become a prerequisite for new gameplay emerging in the AI Agent sector, allowing agents to collaborate in increasingly creative ways—and naturally, new tokens and assets will emerge.
What we can do is keep monitoring progress from leading protocols like Virtuals, and once ecosystem projects begin actively integrating this framework, observe corresponding asset price movements to capture the next opportunity.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News