Hotcoin Research | Market Bets on Rate Cut Probability Exceeding 80% in September: Fed's Q4 Rate Cut Pacing and Impact Outlook
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

Hotcoin Research | Market Bets on Rate Cut Probability Exceeding 80% in September: Fed's Q4 Rate Cut Pacing and Impact Outlook
This article will analyze the basis of the Federal Reserve's interest rate decisions, the impact pathways and historical experiences of rate cuts on crypto assets, and conduct scenario analysis on the probability of a rate cut in September and the pace of rate cuts in the fourth quarter.

1. Introduction
On August 22, Federal Reserve Chair Jerome Powell stated that downside risks to the labor market are rising and that the Fed "may need to adjust our policy stance." Markets widely expect the Fed to begin cutting interest rates at the September FOMC meeting. This comment immediately triggered a strong response from risk assets, with U.S. equities rallying across the board and the crypto market reversing its multi-day downtrend. ETH surged, breaking previous highs and reaching nearly $4,956.
Ultimately, the Fed’s rate decisions hinge on hard data related to employment and inflation. Key dates are now clear: the FOMC meeting is scheduled for September 16–17. The September decision will not only set the interest rate but also update the “dot plot” and macroeconomic forecasts. Two critical pre-meeting data releases—August nonfarm payrolls and unemployment rate (to be released on September 5) and August CPI (September 11)—will largely determine whether a rate cut materializes. This means that over the next three weeks, any surprising data—such as accelerating wage growth, rebounding service-sector inflation, or an unexpectedly low unemployment rate—could disrupt the smooth path of a September cut followed by another later in the year.
This article analyzes the basis of the Fed's interest rate decisions, the pathways through which rate cuts affect crypto assets along with historical precedents, and provides scenario-based projections for the likelihood of a September rate cut and the pace of easing in Q4. It further examines potential crypto market performance and offers investors a multidimensional outlook with probability-weighted forecasts.
2. Determinants of Federal Reserve Interest Rate Policy
The Fed's dual mandate is "maximum employment" and "price stability." Its primary tool for monetary policy is the federal funds rate—the target range for overnight lending rates between U.S. commercial banks, set by the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC). In essence, this is the "wholesale borrowing rate" within the banking system. By adjusting it, the Fed influences the cost of capital and liquidity throughout the financial system, indirectly affecting credit rates, the dollar exchange rate, asset prices, and broader trends in employment and inflation.
Federal Reserve rate policy is jointly constrained by three core factors: employment, inflation, and financial conditions. Monetary policy is not driven by a single indicator but rather represents a dynamic balancing act among multiple variables. Key factors influencing its decisions include labor market indicators (employment numbers, unemployment rate, wage growth), inflation metrics (CPI, core CPI, PCE, inflation expectations), and financial conditions (credit spreads, equity and bond market reactions, financial stability risks). In the current macroeconomic environment of 2025, these combined forces are shifting the Fed from a prolonged period of high rates toward a cautious approach of gradual easing.
1) Rising Labor Market Risks
U.S. nonfarm payrolls increased by only 73,000 in July—significantly below expectations—and prior months’ figures were revised downward. The unemployment rate rose to 4.2%. This suggests the U.S. labor market is approaching "stall speed"—the threshold at which expansion falters—indicating that employment is no longer a reliable buffer for Fed policy. Sustained labor market weakness directly threatens the Fed’s goal of maximum employment, pushing it toward a more dovish policy stance.
2) Inflation Shows Resilience but Remains Generally Moderate
Inflation data shows CPI up 2.7% year-over-year and core CPI up 3.1%, with month-over-month increases of 0.2% and 0.3% respectively. Core CPI posted its largest monthly gain since the start of the year. While inflation remains above the Fed’s 2% target, it has not deteriorated into broad-based reacceleration. Notably, the Producer Price Index (PPI) is trending upward, signaling rising upstream cost pressures, though transmission to final consumer prices remains slow. This pattern of "upstream pressure, downstream moderation" suggests inflation remains sticky in the short term but is not yet out of control.
3) Financial Conditions and Policy Communication
Besides hard data, the Fed closely monitors financial market feedback and stability. Powell’s speech at Jackson Hole clearly signaled that while the Fed is not rushing into aggressive easing, it is leaving room for small adjustments. The core idea is using limited rate cuts to cushion tail risks in the labor market. Markets interpret this as follows: if employment data continues to weaken, the Fed will likely cut rates by 25 basis points in September and possibly make another modest adjustment by year-end.
3. Impact of Rate Policy on Crypto Markets and Historical Analysis
Federal Reserve rate decisions influence not only the dollar and the U.S. economy but also global risk assets—including cryptocurrencies—through multiple layers of financial market transmission. Overall, this transmission occurs through three main channels: the interest rate and discount rate channel, the dollar and capital flows channel, and the risk appetite and investor behavior channel. These interwoven paths collectively shape the cyclical volatility patterns in crypto markets.
1) Discount Rate Channel: Lower Rates Boost Valuation of Risk Assets
Interest rates form the foundation of asset pricing. When the Fed lowers policy rates, Treasury yields decline, reducing the market discount rate. In such an environment, long-duration growth assets—whose value depends heavily on distant future cash flows—see their valuations rise. This explains why tech stocks in the U.S. equity market and digital assets like Bitcoin and Ethereum—often classified as "long-duration assets"—tend to outperform during accommodative cycles. Historically, the Fed’s rapid rate cuts and QE program during the 2020 pandemic directly fueled dual bull markets in equities and crypto, with BTC rising from under $10,000 to $60,000 within a year. Conversely, during the Fed’s aggressive rate hikes in 2022, both Bitcoin and Ethereum lost more than half their value, as rising discount rates suppressed prices.
2) Dollar and Capital Flows Channel: DXY Weakness Benefits Crypto
Fed rate policy also affects capital flows via the strength of the U.S. dollar index (DXY). Rate cuts typically reduce the dollar’s appeal, prompting capital to seek alternative stores of value and higher-yielding assets. In such environments, non-sovereign assets like gold and Bitcoin benefit significantly. For example, when the Fed ended balance sheet reduction and resumed rate cuts in 2019, Bitcoin surged over 100% from its lows during the subsequent DXY decline. In contrast, the Fed’s rate hikes and a strong dollar in 2022 coincided with Bitcoin falling below $20,000. This seesaw relationship between the dollar and Bitcoin has become a key indicator for assessing how policy shifts impact crypto assets.
3) Risk Appetite and Investor Behavior Channel: Equity Markets and ETFs
Rate policy further influences crypto through shifts in stock market risk appetite. Historical data shows a strong positive correlation between Bitcoin and the Nasdaq Composite in most periods. When the Fed signals easing and equities rally, crypto assets often experience amplified upside. Conversely, during equity market sell-offs, crypto tends to suffer exaggerated declines.
Additionally, with the launch of spot Bitcoin and Ethereum ETFs, the link between policy expectations and ETF inflows/outflows has grown tighter. For instance, during the first half of 2024, as the Fed turned dovish, BTC and ETH ETFs recorded sustained net inflows, providing solid support for price gains. However, during periods of heightened policy uncertainty in July and early August, ETFs saw brief net outflows, leading to immediate market corrections. This indicates that ETF fund flows have become a direct transmission mechanism from monetary policy to crypto asset prices.
Since 2019, nearly every major monetary policy turning point has been accompanied by a directional shift in crypto markets, and the inverse correlation between Bitcoin prices and interest rates has become increasingly evident. At the current juncture, with markets broadly betting on a September rate cut, it is crucial to leverage historical insights and transmission mechanisms to understand how the next phase of crypto market dynamics may unfold.
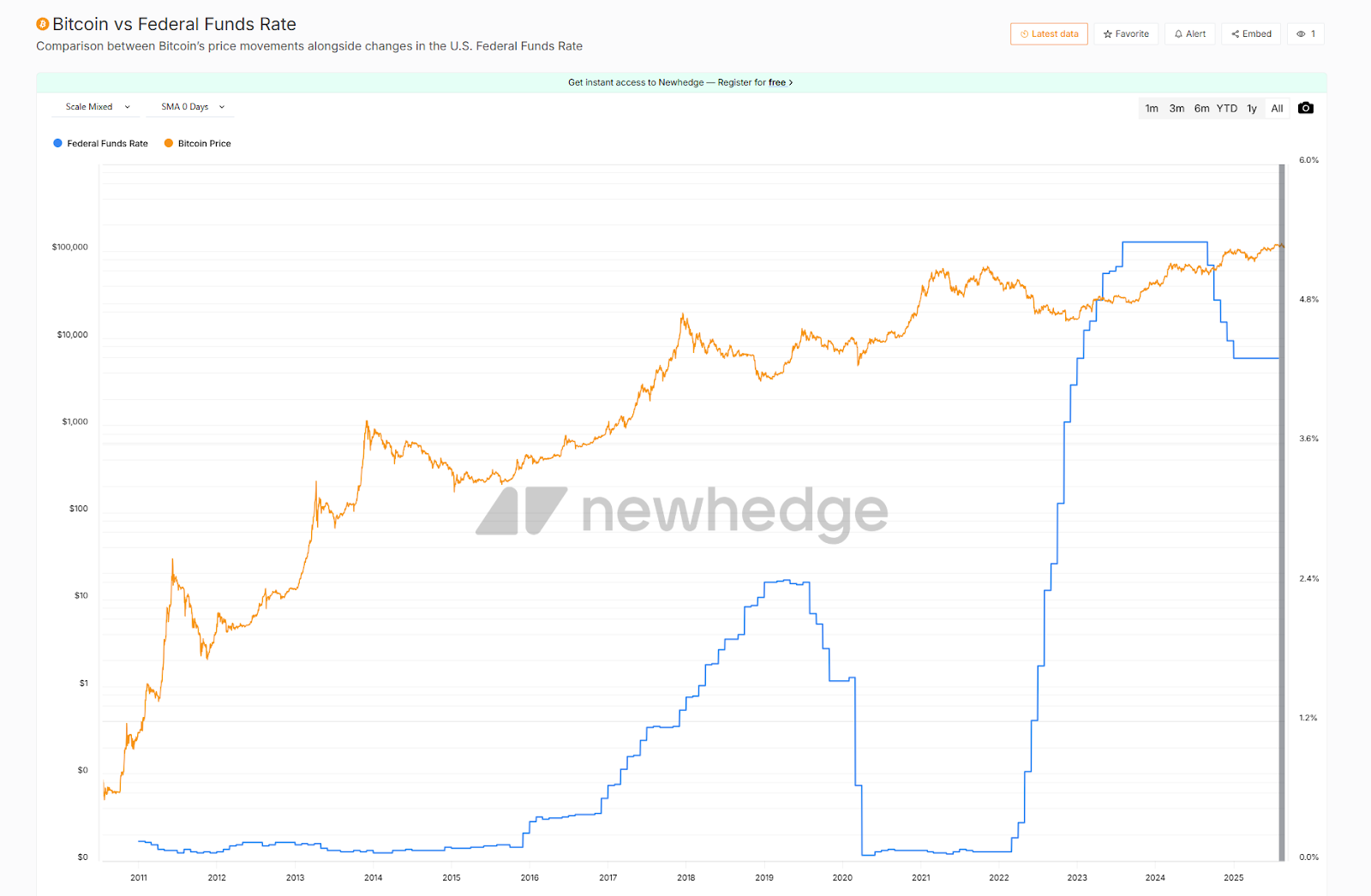
Source: https://newhedge.io/bitcoin/bitcoin-vs-federal-funds-rate
4. Probability and Uncertainty Analysis of a September Rate Cut
The Federal Reserve stands at a pivotal policy crossroads. The September 17 FOMC meeting is more than a routine session—it could signal the direction of monetary policy for all of 2025. Markets are almost fully priced for a 25-basis-point rate cut in September. But the deeper question is: will this be a one-off "insurance cut," or the beginning of a new easing cycle? The answer hinges on two critical upcoming reports—August nonfarm payrolls (to be released September 5) and August CPI (September 11). These data points will directly shape the hawkish or dovish tilt of the Fed’s dot plot and market expectations for the pace of policy in Q4.
1) Likelihood of a September Rate Cut
-
Labor Market: July’s nonfarm payrolls added only 73,000 jobs—far below consensus—and prior months were revised down, with the unemployment rate rising to 4.2%. This indicates a rapidly cooling labor market, nearing "stall speed." If August payrolls remain weak (e.g., below 100,000) and the unemployment rate climbs to 4.3% or higher, the rationale for maintaining high rates will collapse. Slowing job growth signals weakening economic momentum—the most direct catalyst for a policy pivot.
-
Inflation: July CPI was up 2.7% YoY, core CPI up 3.1% YoY, with MoM increases of 0.2% and 0.3% respectively. Although core CPI posted its largest monthly rise this year, inflation has not reignited broadly. If August CPI MoM holds at 0.2% or lower, the Fed will have ample justification to begin cutting rates, citing labor market risks. Even if core CPI rises unexpectedly to 0.3% or higher, it would mainly affect the timing of a year-end cut, not prevent a September move.
-
Market Pricing: CME FedWatch shows an ~87.3% probability of a 25bp cut in September; Polymarket’s prediction market puts it at around 78%. This confirms that a September rate cut is now market consensus.
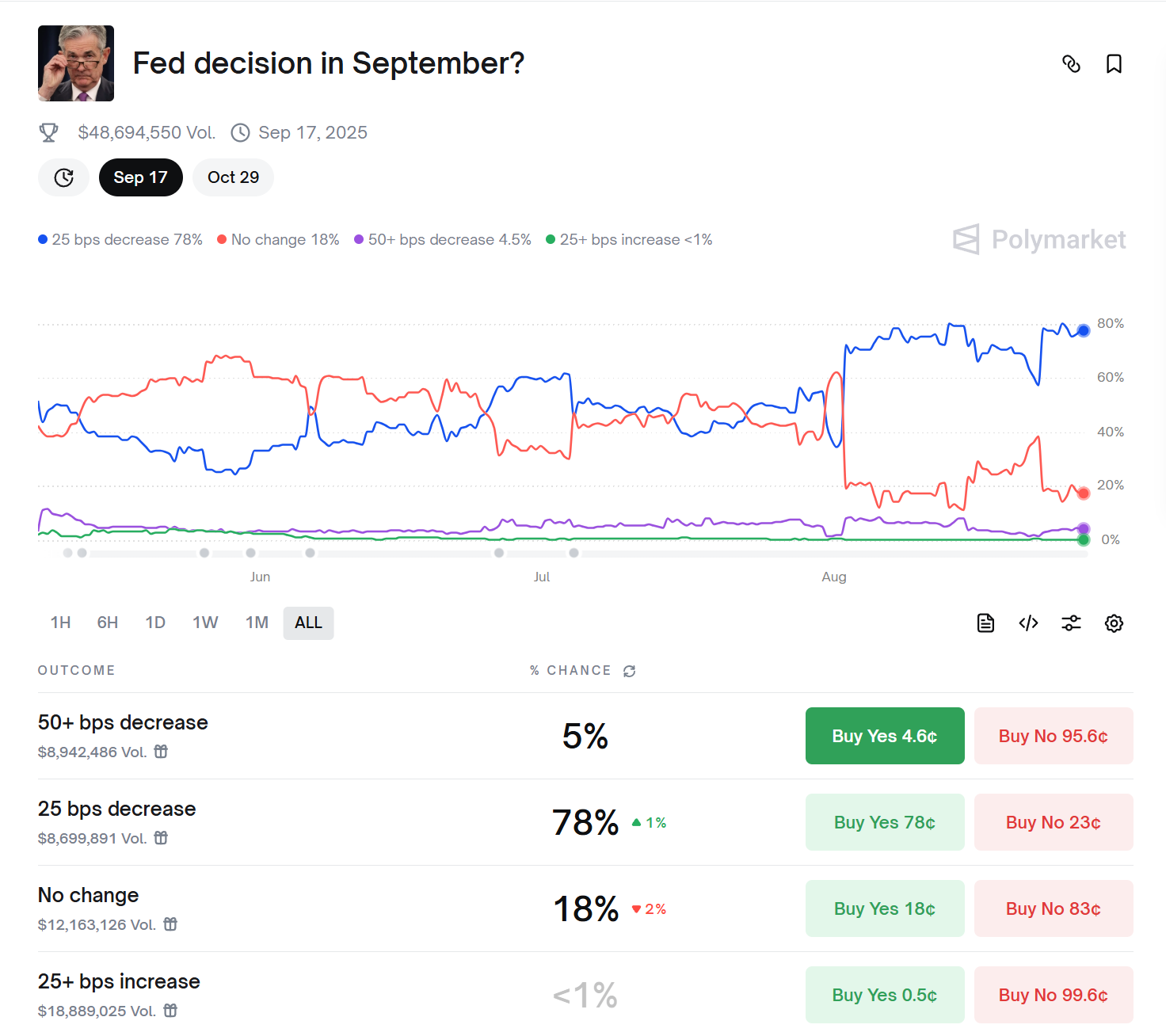
Source: https://polymarket.com/event/fed-decision-in-september
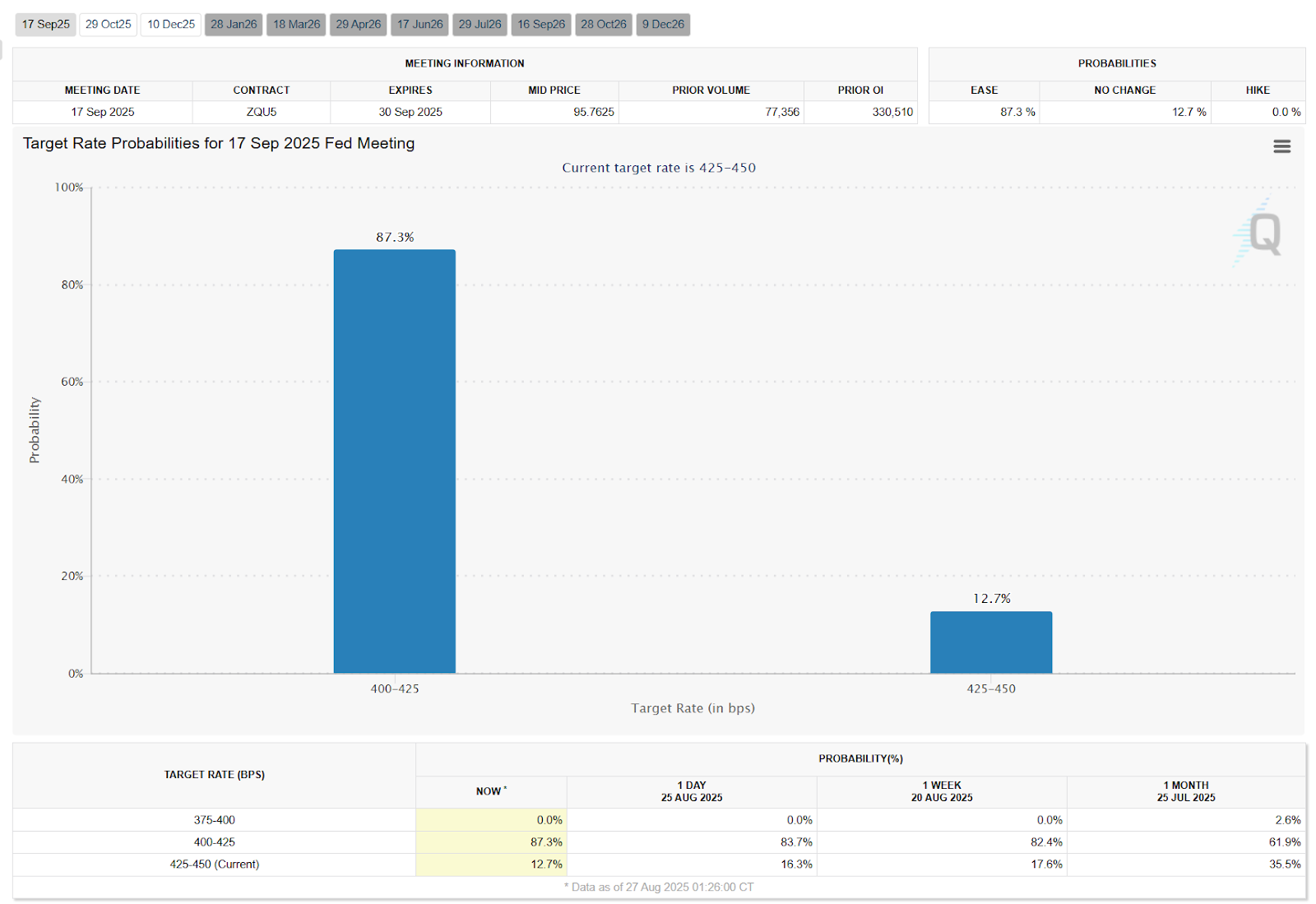
Source: https://www.cmegroup.com/markets/interest-rates/cme-fedwatch-tool.html
Overall, the Fed has little reason to remain on hold in September. Even with persistent inflation stickiness, the central bank appears more concerned about systemic risks from labor market deterioration. Thus, a small rate cut in September is highly probable.
2) Key Uncertainties
While a September cut is likely, the pace of future easing depends on the combination of August data. Three scenarios are possible:
-
Continued Labor Weakness + Moderate Inflation
If August nonfarm payrolls remain below 100,000, unemployment rises above 4.3%, and core CPI MoM ≤0.2%, a 25bp cut in September becomes near-certain, and the probability of another 25bp cut in December increases sharply. This combination implies the Fed must act in September and may add further easing by year-end to stabilize employment. -
Labor Rebound + Sticky Inflation
If August payrolls surprise to the upside (>150,000) and core CPI MoM ≥0.3%, a September cut is still possible (as a hedge against labor market tail risks), but the dot plot tone would turn more hawkish. Markets would interpret this as a "precautionary cut" rather than the start of sustained easing, lowering odds of a second cut by year-end. -
Misalignment Between Labor and Inflation
If employment improves while inflation falls, or vice versa, the policy path becomes more complex. For example, a resurgence of wage growth and sticky service inflation might prompt the Fed to signal caution in September, or even delay action until October. Though unlikely, such an outcome would trigger significant short-term market volatility.
Overall, a 25bp rate cut in September is highly certain, with both market pricing and policy communication paving the way. However, the pace in Q4 remains uncertain, hinging on whether employment worsens further and inflation stays moderate. If both soft employment and slowing inflation persist, the Fed will cut faster. If inflation proves stubborn, the pace will slow, potentially limiting cuts to just one.
5. Q4 Outlook: Three Scenario Projections and Market Implications
If a September rate cut is largely assured, the real question lies in the pace from October to December. This depends on whether employment deteriorates further and whether inflation remains subdued. Based on these two variables, we can project three policy paths:
(A) Base Case: 50bp total cuts in September and December (~55% probability)
-
Conditions: August payrolls remain weak, core CPI stays moderate.
-
Pace: September -25bp → October pause → December -25bp.
-
Market Implication: Aligns with consensus Wall Street forecasts (50bp total for the year). For crypto, this implies steady improvement in liquidity and a gradual, rather than explosive, upward trend.
(B) Cautious Case: Only one cut in September (~30% probability)
-
Conditions: August CPI MoM ≥0.3%, sticky service inflation; labor market does not worsen further.
-
Pace: September -25bp → Q4 pause.
-
Market Implication: Short-term利好 realized, but a hawkish dot plot caps optimism. Crypto may trade sideways, with capital rotating into thematic sectors but lacking sustained momentum.
(C) Surprise Case: Accelerated easing in Q4 (~15% probability)
-
Conditions: August payrolls extremely weak (<50k), unemployment nearing 4.5%, while core CPI declines.
-
Pace: September -25bp → October and December cuts, total annual cuts ≥75bp.
-
Market Implication: Unexpectedly loose liquidity fuels broad risk-on sentiment. Crypto could see a 2020-style explosive bull run, with Bitcoin and Ethereum quickly making new highs and altcoins and DeFi entering high-volatility phases. However, if economic deterioration runs deep, both equities and crypto may first experience sharp volatility before resuming upward movement.
The key difference among these scenarios lies in the combination of labor and inflation outcomes. The base case is most likely (moderate easing), while cautious and surprise cases represent slower and faster pacing, respectively. For investors, the data releases on September 5 and 11 will not only determine the September FOMC decision but also shape market expectations for the rest of the year.
Conclusion
In summary, the U.S. economic mix of "slowing employment and unsettled inflation" is pushing the Federal Reserve toward a turning point, making a September start to the easing cycle highly probable. This macro pivot is undoubtedly a major positive for the crypto market, which has faced pressure over the past two years. Declining interest rates will lift the overhang on risk assets like Bitcoin and restore confidence in liquidity and growth. The market’s swift reaction following Powell’s dovish hint shows that capital is already positioning for a new cycle. The crypto market now stands at a critical juncture where macro policy and industry developments converge. With macro easing coinciding with increasing mainstream adoption, the stage is set for a new market phase.
However, as this article has detailed, the Fed’s policy impact on crypto is multifaceted—bringing both opportunities from rising liquidity and volatility from expectation-driven trading. Investors should closely monitor upcoming employment and inflation data, watching whether policy signals align with market expectations. Chain data and market indicators show institutions and large holders are already positioning early, but short-term pullbacks and chip exchanges continue to occur frequently, suggesting the path ahead won’t be smooth. Over the coming months, the most likely scenario is that an accommodative rate environment will provide sustained upward momentum for crypto. Whether the outcome is an accelerated bull run or a delayed easing, achieving consistent returns will depend on dynamic strategy adjustments and disciplined risk management. Monitoring early-September labor and inflation data and the Fed’s policy progress, and updating views promptly with new information, will be essential. Maintaining caution when consensus is strong and having the courage to position contrarily during panic will be key to navigating uncertainty successfully.
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News













