Coinbase Mid-Year Review: 10 Charts Showing the State of the Crypto Market, Short-Term Frenzy Has Faded
TechFlow Selected TechFlow Selected

Coinbase Mid-Year Review: 10 Charts Showing the State of the Crypto Market, Short-Term Frenzy Has Faded
Overall, TVL growth year-to-date has outpaced the total market cap growth of the crypto market by 24%. TON, Aptos, Sui, and Base are relatively new and are currently in a rapid growth phase.
Author: David Han
Compiled by: TechFlow
Summary
In our mid-year review, we present 10 charts covering key fundamentals and technological trends in the crypto market. We begin by examining total value locked (TVL) growth relative to native gas token price appreciation across top Layer-1 (L1) and Layer-2 (L2) networks. Then, we comparatively assess on-chain activity drivers—transaction fees and active addresses—across these networks, followed by a detailed analysis of Ethereum's primary fee drivers. We also review on-chain supply dynamics, correlations, and current liquidity conditions in both spot and futures crypto markets.
Another closely watched metric in crypto is inflows and outflows from U.S. spot Bitcoin ETFs, often seen as a proxy for shifts in crypto demand. However, the year-to-date growth in open interest (OI) of CME Bitcoin futures suggests that since the ETF launch, part of the inflows has been driven by basis trading. By isolating the impact of CME futures basis trades, we show that non-hedged exposure to BTC ETFs has grown significantly more slowly since early April.
Fundamental Signals
-
TVL Growth
Rather than comparing raw TVL across different chains directly, we track TVL growth normalized by the price growth of their native gas tokens. Native tokens often constitute a large portion of ecosystem TVL due to staking or liquidity purposes. Adjusting TVL growth by price appreciation helps isolate how much growth stems from net new value creation rather than pure price increases.
Overall, TVL growth year-to-date has outpaced the crypto market cap increase by 24%. The fastest-growing chains—TON, Aptos, Sui, and Base—are relatively new and still in rapid expansion phases.
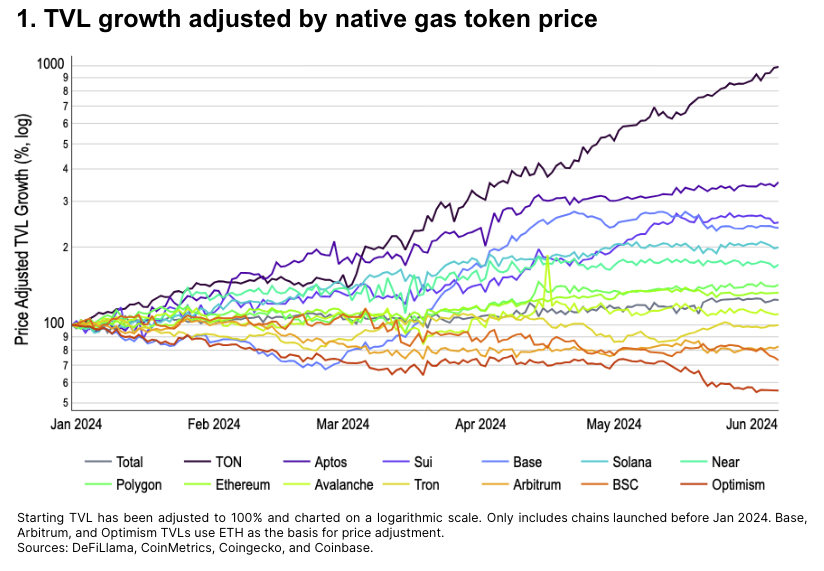
-
Activity Drivers: Fees and Users
We compare each network’s average daily active addresses in May against its average daily fees or revenue, both measured in standard deviations relative to the prior four months (January–April). Key findings:
-
Chain fees declined across most networks in May, except for Solana and Tron.
-
Following EIP-4844, lower fees led to a significant rise in active addresses on Ethereum L2s, particularly Arbitrum.
-
Fees on Cardano and Binance Smart Chain dropped less than wallet activity declines.
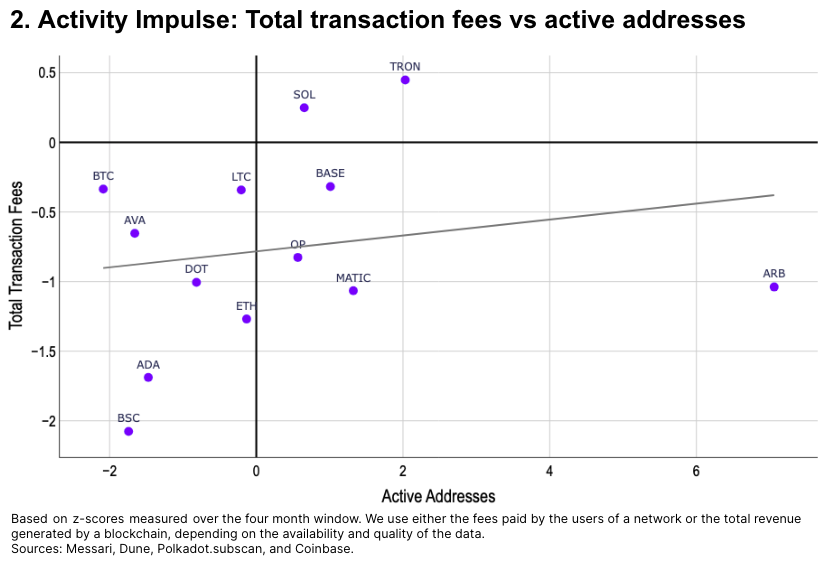
-
Transaction Fee Drivers
We categorized fee spending across the top 50 contracts on Ethereum, which account for over 55% of total gas fees year-to-date.
Since the Dencun upgrade in March, fees paid by Rollups have fallen from 12% of mainnet fees to under 1%. MEV-driven activity rose from 8% to 14%, while direct transaction fees increased from 20% to 36%. Although ETH turned inflationary since mid-April, we believe a return in market volatility—and demand for high-value transaction blocks—could offset this trend.
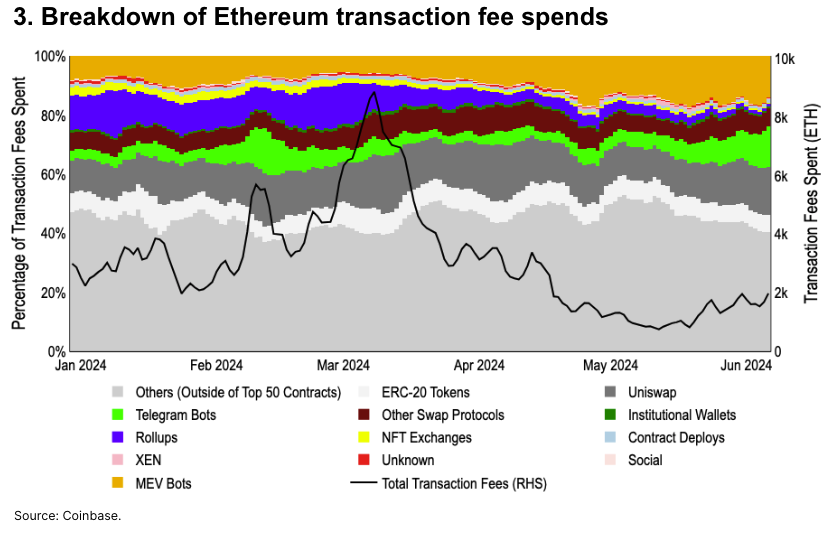
-
Ethereum L2 Growth
Year-to-date, Ethereum L2 TVL has grown 2.4x, reaching $9.4 billion by the end of May. As of early June, Base accounts for about 19% of total L2 TVL, trailing Arbitrum (33%) and Blast (24%).
Meanwhile, total transaction fees have dropped significantly since the Dencun upgrade introduced blob storage on March 13—even as TVL (and transaction counts on many chains) reached all-time highs.
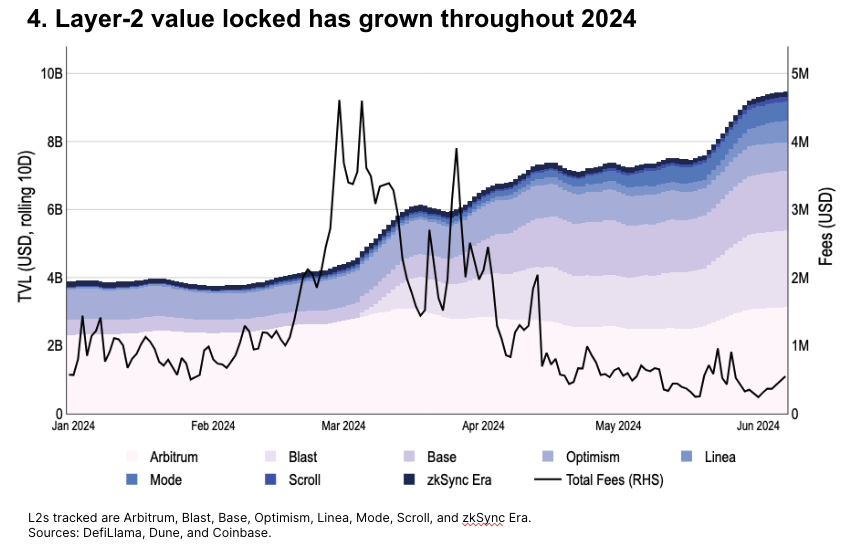
-
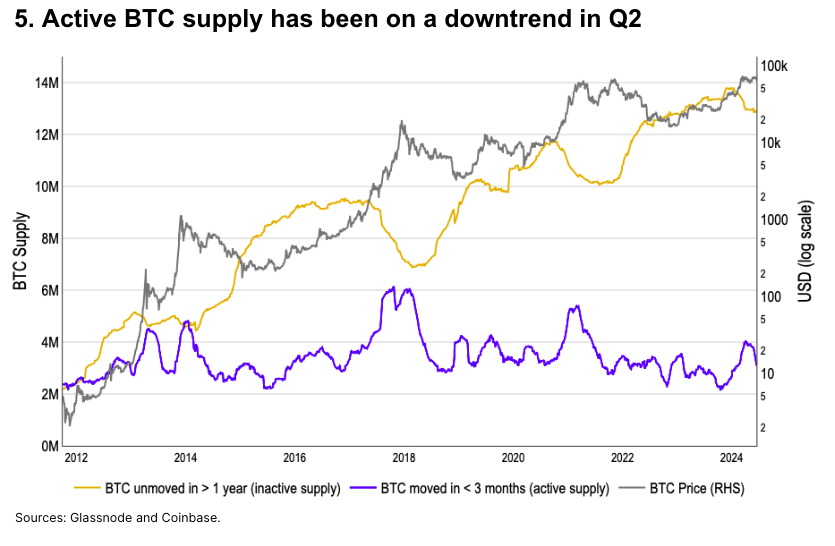
Bitcoin Active Supply Trends
We define active BTC supply as BTC moved within the past three months, which typically declines after local price peaks—indicating slowing market turnover. Active BTC supply peaked locally at 4 million BTC in early April—the highest level since H1 2021—then fell to 3.1 million by early June.
However, BTC supply dormant for over one year has remained stable year-to-date. This suggests short-term speculative fervor has cooled, while long-term cyclical investors remain engaged.
Technical Signals
-
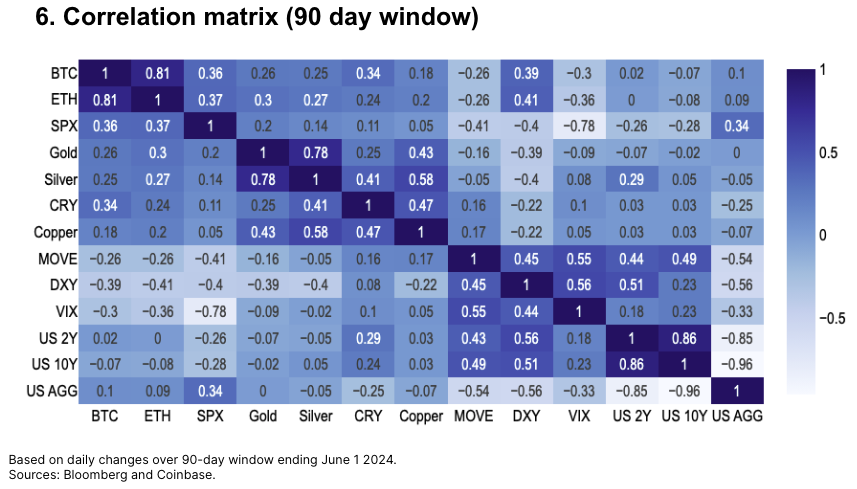
Correlations
Over a 90-day window, Bitcoin returns show moderate correlation with daily changes in key macro factors—U.S. equities, commodities, and the multilateral dollar index—though the positive link with gold remains relatively weak.
Meanwhile, Ethereum’s correlation with S&P 500 returns (0.37) is nearly identical to Bitcoin’s (0.36). Crypto-crypto trading remains highly correlated, though BTC/ETH correlation has slightly dipped from a peak of 0.85 in March–April to 0.81.
-
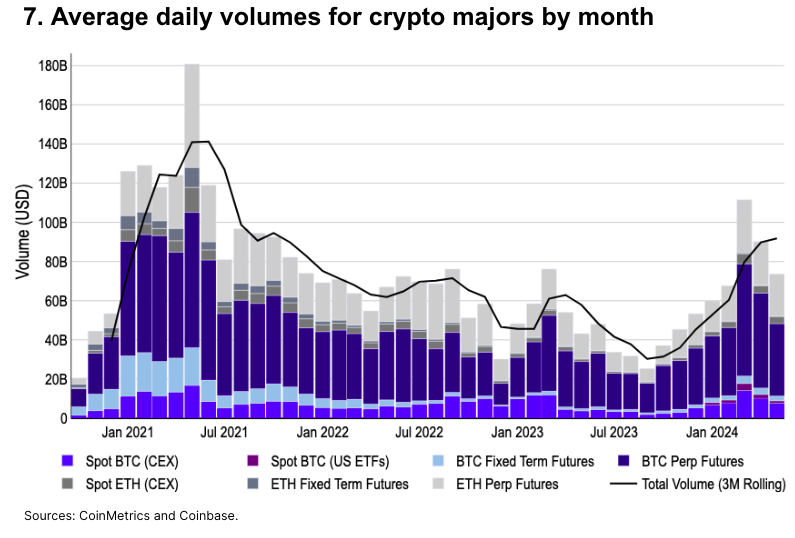
Increased Market Liquidity
Average daily combined spot and futures trading volume for Bitcoin and Ethereum dropped 34% from its March 2024 peak of $111.5 billion. Nonetheless, May’s volume ($74.6 billion) exceeded every month since September 2022, except March 2023.
After the January approval of U.S. spot Bitcoin ETFs, spot Bitcoin volume surged. In May, centralized exchange (CEX) Bitcoin spot volume was 50% higher than in December ($7.6B vs $5.1B). May’s spot Bitcoin ETF volume reached $1.2 billion, accounting for 14% of global spot volume.
-
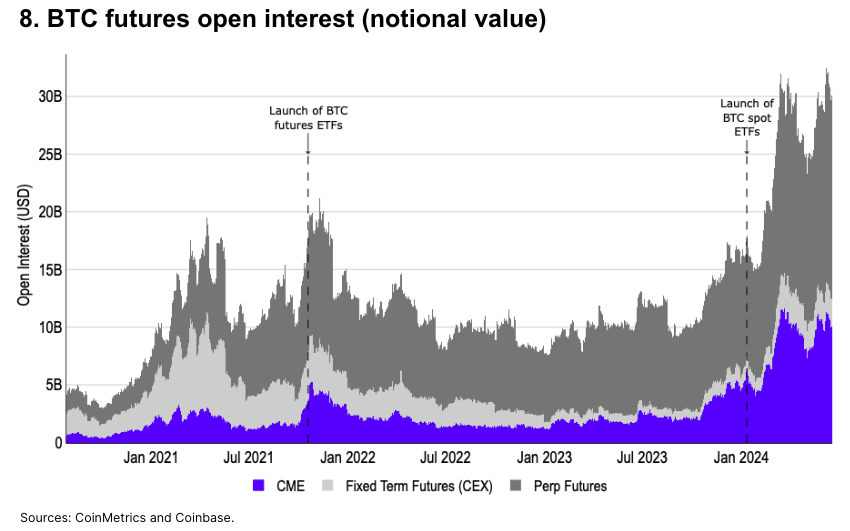
CME Bitcoin Futures
Since the beginning of 2024, CME open interest (OI) has grown 2.2x (from $4.5B to $9.7B), and 8.1x since the start of 2023 (from $1.2B to $9.7B). We believe much of the year-to-date inflow can be attributed to basis trading following the spot ETF approval. With the launch of spot ETFs, Bitcoin basis trading can now be fully conducted in the U.S. via traditional securities brokers.
Perpetual contract OI also rose from $9.8B to $16.6B, with CME OI maintaining a share of around 30% (29–32%) year-to-date. Still, CME futures have notably increased their market share—from 16% at the start of 2023 to 30% today—indicating rising institutional interest from U.S.-based players.
-
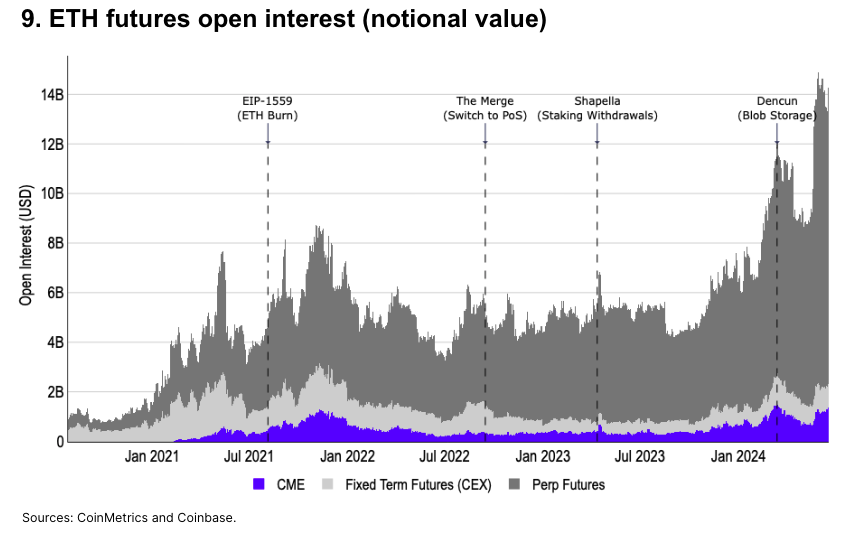
CME Ethereum Futures
CME ETH futures OI is near all-time highs. However, ETH OI remains dominated by perpetual futures available in certain non-U.S. jurisdictions. As of June 1, 85% ($12.1B) of total OI comes from perps, while CME futures account for only 8% ($1.1B).
Endogenous ETH catalysts clearly impact OI. The last major OI spike followed the approval of the U.S. spot ETH ETF (Form 19b-4). Prior to that, OI peaked around the Dencun upgrade on March 13.
Additionally, traditional fixed-term futures on centralized exchanges remain popular, with OI levels comparable to CME futures.
-
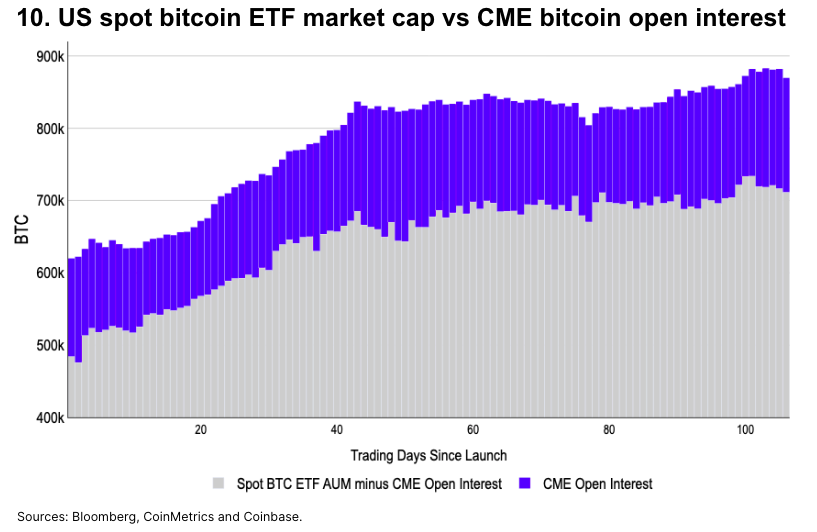
Isolating CME Bitcoin Basis Trades
Normalizing total spot ETF market cap against CME Bitcoin OI suggests that much of the spot ETF inflow since early April can be attributed to basis trading.
After ETF approval, BTC held in ETF custody increased by approximately 200,000 BTC by March 13 (Day 43), indicating directional BTC buying during that period—partially explaining the price surge. Since then, BTC in ETF custody has remained between 825,000 and 850,000, only decisively breaking above this range in late May.
Join the official TechFlow community
Telegram subscription group:
Official Twitter account:
English Twitter account:
Join TechFlow official community to stay tuned
Telegram:https://t.me/TechFlowDaily
X (Twitter):https://x.com/TechFlowPost
X (Twitter) EN:https://x.com/BlockFlow_News